White-matter lesions along the cholinergic tracts are related to cortical sources of EEG rhythms in amnesic mild cognitive impairment
- PMID: 19097164
- PMCID: PMC6871072
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20612
White-matter lesions along the cholinergic tracts are related to cortical sources of EEG rhythms in amnesic mild cognitive impairment
Abstract
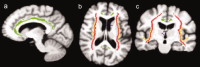
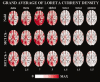
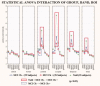
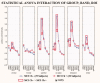
Does impairment of cholinergic systems represent an important factor in the development of amnesic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), as a preclinical stage of Alzheimer's disease (AD)? Here we tested the hypothesis that electroencephalographic (EEG) rhythms, known to be modulated by the cholinergic system, may be particularly affected in aMCI patients with lesions along the cholinergic white-matter tracts. Eyes-closed resting EEG data were recorded in 28 healthy elderly (Nold) and 57 aMCI patients. Lesions along the cholinergic white-matter tracts were detected with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences on magnetic resonance imaging. The estimation of the cholinergic lesion was performed with a validated semi-automatic algorithm pipeline after registration to a stereotactic template, image integration with stereotactic masks of the cholinergic tracts, and normalization to intracranial volume. The aMCI patients were divided into two groups of high (MCI Ch+; N = 29; MMSE = 26.2) and low cholinergic damage (MCI Ch-; N = 28; MMSE = 26.6). EEG rhythms of interest were delta (2-4 Hz), theta (4-8 Hz), alpha 1 (8-10.5 Hz), alpha 2 (10.5-13 Hz), beta 1 (13-20 Hz), and beta 2 (20-30 Hz). Cortical EEG generators were estimated by LORETA software. As main results, (i) power of occipital, parietal, temporal, and limbic alpha 1 sources was maximum in Nold, intermediate in MCI Ch-, and low in MCI Ch+ patients; (ii) the same trend was true in theta sources. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that damage to the cholinergic system is associated with alterations of EEG sources in aMCI subjects.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M,Smith LA,Scherr PA,Taylor JO,Evans DA,Funkenstein HH ( 1991): Use of brief cognitive tests to identify individuals in the community with clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease. Int J Neurosci 57: 167–178. - PubMed
-
- Anderer P,Saletu B,Pascual‐Marqui RD ( 2000): Effect of the 5‐HT(1A) partial agonist buspirone on regional brain electrical activity in man: a functional neuroimaging study using low‐resolution electromagnetic tomography (LORETA). Psychiatry Res 100: 81–96. - PubMed
-
- Anderer P,Saletu B,Semlitsch HV,Pascual‐Marqui RD ( 2003): Non‐invasive localization of P300 sources in normal aging and age‐associated memory impairment. Neurobiol Aging 24: 463–479. - PubMed
-
- Anderer P,Saletu B,Saletu‐Zyhlarz G,Gruber D,Metka M,Huber J,Pascual‐Marqui RD ( 2004): Brain regions activated during an auditory discrimination task in insomniac postmenopausal patients before and after hormone replacement therapy: Low‐resolution brain electromagnetic tomography applied to event‐related potentials. Neuropsychobiology 49: 134–153. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P,Morris R,Amaral D,Bliss T,O'Keefe J ( 2007): The Hippocampus Book. New York: Oxford University Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

