Whole-body imaging at 7T: preliminary results
- PMID: 19097214
- PMCID: PMC2875945
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.21751
Whole-body imaging at 7T: preliminary results
Abstract
The objective of this study was to investigate the feasibility of whole-body imaging at 7T. To achieve this objective, new technology and methods were developed. Radio frequency (RF) field distribution and specific absorption rate (SAR) were first explored through numerical modeling. A body coil was then designed and built. Multichannel transmit and receive coils were also developed and implemented. With this new technology in hand, an imaging survey of the "landscape" of the human body at 7T was conducted. Cardiac imaging at 7T appeared to be possible. The potential for breast imaging and spectroscopy was demonstrated. Preliminary results of the first human body imaging at 7T suggest both promise and directions for further development.
Figures

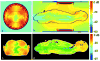
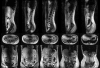
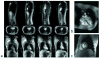

References
-
- Vaughan J, Adriany G, Snyder C, Tian J, Thiel T, Bolinger L, Liu H, DelaBarre L, Ugurbil K. Efficient high-frequency body coil for high-field MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2004;52:851–859. - PubMed
-
- Vaughan J, Garwood M, Collins C, DelaBarre L, Adriany G, Andersen P, Merkle H, Smith M, Ugurbil K. 7T vs. 4T: RF power, homogeneity & signal-to-noise comparison in head images. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:24–30. - PubMed
-
- Yacoub E, Shmuel A, Pfeuffer J, Van de Moortele PF, Adriany G, Andersen P, Vaughan JT, Merkle H, Ugurbil K, Hu XP. Imaging brain function in humans at 7 Tesla. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2001;45(4):588–594. - PubMed
-
- Van de Moortele PF, Akgun C, Adriany G, Moeller S, Ritter J, Collins C, Smith M, Vaughan J, Ugurbil K. B1 destructive interferences and spatial phase patterns at 7 tesla with a head transceiver array coil. Magn Reson Med. 2005;54(6):1503–1518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

