Absence of alpha-synuclein affects dopamine metabolism and synaptic markers in the striatum of aging mice
- PMID: 19097673
- PMCID: PMC3146702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.11.001
Absence of alpha-synuclein affects dopamine metabolism and synaptic markers in the striatum of aging mice
Abstract
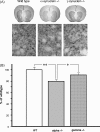
Despite numerous evidences for neurotoxicity of overexpressed alpha-synuclein, a protective function was suggested for endogenous alpha-synuclein and other members of the synuclein family. This protective role is most important for and evident in presynaptic terminals, where synucleins are normally accumulated. However, mice lacking synucleins display no adverse phenotype. In particular, no significant changes in striatal dopamine metabolism and only subtle deficit of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra were found in juvenile or adult mice. To assess whether aging and synuclein deficiency may have additive detrimental effect on the nigrostriatal system, we studied dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra and their striatal synapses in 24-26-month-old alpha-synuclein and gamma-synuclein null mutant mice. Significant approximately 36% reduction of the striatal dopamine was found in aging alpha-synuclein, but not gamma-synuclein null mutant mice when compared to age-matching wild type mice. This was accompanied by the reduction of TH-positive fibers in the striatum and decrease of striatal levels of TH and DAT. However, no progressive loss of TH-positive neurons was revealed in the substantia nigra of synuclein-deficient aging animals. Our results are consistent with a hypothesis that alpha-synuclein is important for normal function and integrity of synapses, and suggest that in the aging nervous system dysfunction of this protein could become a predisposition factor for the development of nigrostriatal pathology.
(c) 2008 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


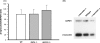
References
-
- Abeliovich A., Schmitz Y., Farinas I., Choi-Lundberg D., Ho W.H., Castillo P.E., Shinsky N., Verdugo J.M., Armanini M., Ryan A., Hynes M., Phillips H., Sulzer D., Rosenthal A. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Abercrombie M. Estimation of nicear population from microtome sections. Anat. Rec. 1946;94:239–247. - PubMed
-
- Altar C.A., Marien M.R., Marshall J.F. Time course of adaptations in dopamine biosynthesis, metabolism, and release following nigrostriatal lesions: implications for behavioral recovery from brain injury. J. Neurochem. 1987;48:390–399. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Fischer D., Henze C., Strenzke C., Westrich J., Ferger B., Hoglinger G.U., Oertel W.H., Hartmann A. Characterization of the striatal 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease in wild type and alpha-synuclein-deleted mice. Exp. Neurol. 2008;210:182–193. - PubMed
-
- Benno R.H., Tucker L.W., Joh T.H., Reis D.J. Quantitative immunocytochemistry of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain. I. Development of a computer assisted method using the peroxidase-antiperoxidase technique. Brain Res. 1982;246:225–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

