Bcl-2 family proteins contribute to apoptotic resistance in lung cancer multicellular spheroids
- PMID: 19097992
- PMCID: PMC2701959
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0320OC
Bcl-2 family proteins contribute to apoptotic resistance in lung cancer multicellular spheroids
Abstract
Combinatorial therapies using the proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, have been found to induce synergistic apoptosis in cancer cells grown as monolayers; however, three-dimensional spheroid culture may be a better model for the multicellular resistance found in solid tumors, such as lung cancer. We tested the combinatorial apoptotic strategy of using bortezomib together with TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), both in monolayers and in spheroids of A549 lung cancer cells. Indeed, bortezomib plus TRAIL induced synergistic apoptosis in A549 cells grown as monolayers, but had little effect on A549 cells grown as three-dimensional multicellular spheroids. The acquired resistance of spheroids was not due to a limitation of diffusion, to survival pathways, such as NF-kappaB or PI3K/Akt/mTOR, or to the up-regulation of FLIP(S) (Fas-associated death domain-like IL-1 beta-converting enzyme inhibitory protein, short). We then investigated a role for the Bcl-2 family of anti- and proapoptotic proteins. When cells formed spheroids, antiapoptotic Bcl-2 increased, whereas antiapoptotic Mcl-1 decreased. ABT-737, a small molecule that inhibits Bcl-2, but not Mcl-1, abolished the multicellular resistance of A549 spheroids to bortezomib plus TRAIL. In another lung cancer cell line, H1299, acquisition of multicellular resistance in spheroids was also accompanied by an increase in Bcl-2 and decrease in Mcl-1. In H1299 spheroids compared with those of A549, however, Mcl-1 remained higher, and Mcl-1 knockdown was more effective than ABT-737 in removing multicellular resistance. Our study suggests that the balance of Bcl-2 family proteins contributes to the acquired multicellular resistance of spheroids, and suggests a possible target for improving the response of lung cancer to bortezomib therapies.
Figures
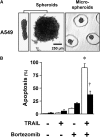

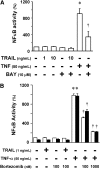
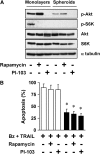
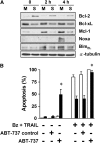
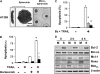
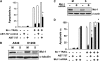
Comment in
-
Rounding up apoptosis resistance targets in lung cancer.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Jul;41(1):7-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0002ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19525385 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bremer E, van Dam G, Kroesen BJ, de Leij L, Helfrich W. Targeted induction of apoptosis for cancer therapy: current progress and prospects. Trends Mol Med 2006;12:382–393. - PubMed
-
- Broaddus VC, Dansen TB, Abayasiriwardana KS, Wilson SM, Finch AJ, Swigart LB, Hunt AE, Evan GI. Bid mediates apoptotic synergy between tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis–inducing ligand (TRAIL) and DNA damage. J Biol Chem 2005;280:12486–12493. - PubMed
-
- Lowe SW, Cepero E, Evan GI. Intrinsic tumour suppression. Nature 2004;432:307–315. - PubMed
-
- Milligan SA, Nopajaroonsri C. Inhibition of NF-kappa B with proteasome inhibitors enhances apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res 2001;21:39–44. - PubMed
-
- An J, Sun Y, Fisher M, Rettig MB. Maximal apoptosis of renal cell carcinoma by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is nuclear factor-kappaB dependent. Mol Cancer Ther 2004;3:727–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

