Discovery and revision of Arabidopsis genes by proteogenomics
- PMID: 19098097
- PMCID: PMC2605632
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0811066106
Discovery and revision of Arabidopsis genes by proteogenomics
Abstract
Gene annotation underpins genome science. Most often protein coding sequence is inferred from the genome based on transcript evidence and computational predictions. While generally correct, gene models suffer from errors in reading frame, exon border definition, and exon identification. To ascertain the error rate of Arabidopsis thaliana gene models, we isolated proteins from a sample of Arabidopsis tissues and determined the amino acid sequences of 144,079 distinct peptides by tandem mass spectrometry. The peptides corresponded to 1 or more of 3 different translations of the genome: a 6-frame translation, an exon splice-graph, and the currently annotated proteome. The majority of the peptides (126,055) resided in existing gene models (12,769 confirmed proteins), comprising 40% of annotated genes. Surprisingly, 18,024 novel peptides were found that do not correspond to annotated genes. Using the gene finding program AUGUSTUS and 5,426 novel peptides that occurred in clusters, we discovered 778 new protein-coding genes and refined the annotation of an additional 695 gene models. The remaining 13,449 novel peptides provide high quality annotation (>99% correct) for thousands of additional genes. Our observation that 18,024 of 144,079 peptides did not match current gene models suggests that 13% of the Arabidopsis proteome was incomplete due to approximately equal numbers of missing and incorrect gene models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

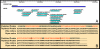

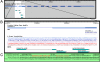
References
-
- Kellis M, Patterson N, Endrizzi M, Birren B, Lander ES. Sequencing and comparison of yeast species to identify genes and regulatory elements. Nature. 2003;423:241–254. - PubMed
-
- Brent MR. Steady progress and recent breakthroughs in the accuracy of automated genome annotation. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:62–73. - PubMed
-
- Baerenfaller K, et al. Genome-scale proteomics reveals Arabidopsis thaliana gene models and proteome dynamics. Science. 2008;320:938–941. - PubMed
-
- Brunner E, et al. A high-quality catalog of the Drosophila melanogaster proteome. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:576–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

