Structural basis for cross-resistance to ribosomal PTC antibiotics
- PMID: 19098107
- PMCID: PMC2605634
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810826105
Structural basis for cross-resistance to ribosomal PTC antibiotics
Abstract
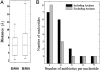
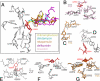
Clinically relevant antibiotics that target the ribosomal peptidyl transferase center (PTC), a highly conserved ribosomal region, exert their inhibitory action by exploiting the flexibility of PTC nucleotides, which trigger modulations of the shape of the antibiotic binding pocket. Resistance to these antibiotics was observed clinically and in vitro. Based on the crystal structures of the large ribosomal subunit from eubacterium suitable to represent pathogens in complex with these antibiotics, it was found that all nucleotides mediating resistance to PTC antibiotics cluster on one side of the PTC. Over half of the nucleotides affecting resistance reside in regions of lower sequence conservation, and are too distal to make Van der Waals interactions with the bound drugs. Alterations of the identity of these nucleotides may not lethally affect ribosome function, but can hamper antibiotic binding through changes in the conformation and flexibility of specific PTC nucleotides. Comparative analysis revealed properties likely to lead to cross-resistance and enabled their parameterization. As the same nucleotides are frequently involved in resistance to more than a single family of antibiotics, the common pattern explains medically observed cross-resistance to PTC antibiotics and suggests the potential for a wider clinical threat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
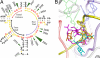
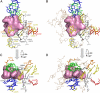
Similar articles
-
Structures of the Escherichia coli ribosome with antibiotics bound near the peptidyl transferase center explain spectra of drug action.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 5;107(40):17152-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007988107. Epub 2010 Sep 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20876128 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of peptide bond formation by pleuromutilins: the structure of the 50S ribosomal subunit from Deinococcus radiodurans in complex with tiamulin.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Dec;54(5):1287-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04346.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15554968
-
High-resolution structures of large ribosomal subunits from mesophilic eubacteria and halophilic archaea at various functional States.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002 Feb;3(1):67-78. doi: 10.2174/1389203023380828. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002. PMID: 12370012 Review.
-
Structural insights into the roles of water and the 2' hydroxyl of the P site tRNA in the peptidyl transferase reaction.Mol Cell. 2005 Nov 11;20(3):437-48. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.006. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 16285925
-
Antibiotics targeting ribosomes: resistance, selectivity, synergism and cellular regulation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:649-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133130. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16180279 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping the in vivo fitness landscape of a tethered ribosome.Sci Adv. 2023 Apr 28;9(17):eade8934. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade8934. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37115918 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal Antibiotics: Contemporary Challenges.Antibiotics (Basel). 2016 Jun 29;5(3):24. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics5030024. Antibiotics (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27367739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GPU/CPU Algorithm for Generalized Born/Solvent-Accessible Surface Area Implicit Solvent Calculations.J Chem Theory Comput. 2012 Jul 10;8(7):2521-2530. doi: 10.1021/ct3003089. Epub 2012 Jun 15. J Chem Theory Comput. 2012. PMID: 23049488 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of ribosome-lankacidin complex reveals ribosomal sites for synergistic antibiotics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 2;107(5):1983-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914100107. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080686 Free PMC article.
-
The development of peptide ligands that target helix 69 rRNA of bacterial ribosomes.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Sep 15;24(18):4486-4491. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.07.050. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27492196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bashan A, Yonath A. Correlating ribosome function with high-resolution structures. Trends Microbiol. 2008;9:326–335. - PubMed
-
- Schleunzen F, et al. Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature. 2001;413:814–821. - PubMed
-
- Tu D, Blaha G, Moore PB, Steitz TA. Structures of MLSBK antibiotics bound to mutated large ribosomal subunits provide a structural explanation for resistance. Cell. 2005;121:257–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

