N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline prevents cardiac remodeling and dysfunction induced by galectin-3, a mammalian adhesion/growth-regulatory lectin
- PMID: 19098114
- PMCID: PMC2643891
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00747.2008
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline prevents cardiac remodeling and dysfunction induced by galectin-3, a mammalian adhesion/growth-regulatory lectin
Abstract
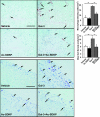
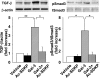
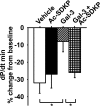
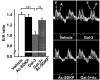
Galectin-3 (Gal-3) is secreted by activated macrophages. In hypertension, Gal-3 is a marker for hypertrophic hearts prone to develop heart failure. Gal-3 infused in pericardial sac leads to cardiac inflammation, remodeling, and dysfunction. N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (Ac-SDKP), a naturally occurring tetrapeptide, prevents and reverses inflammation and collagen deposition in the heart in hypertension and heart failure postmyocardial infarction. In the present study, we hypothesize that Ac-SDKP prevents Gal-3-induced cardiac inflammation, remodeling, and dysfunction, and these effects are mediated by the transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta/Smad3 signaling pathway. Adult male rats were divided into four groups and received the following intrapericardial infusion for 4 wk: 1) vehicle (saline, n = 8); 2) Ac-SDKP (800 microg x kg(-1) x day(-1), n = 8); 3) Gal-3 (12 microg/day, n = 7); and 4) Ac-SDKP + Gal-3 (n = 7). Left ventricular ejection fraction, cardiac output, and transmitral velocity were measured by echocardiography; inflammatory cell infiltration, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, and collagen deposition in the heart by histological and immunohistochemical staining; and TGF-beta expression and Smad3 phosphorylation by Western blot. We found that, in the left ventricle, Gal-3 1) enhanced macrophage and mast cell infiltration, increased cardiac interstitial and perivascular fibrosis, and causes cardiac hypertrophy; 2) increased TGF-beta expression and Smad3 phosphorylation; and 3) decreased negative change in pressure over time response to isoproterenol challenge, ratio of early left ventricular filling phase to atrial contraction phase, and left ventricular ejection fraction. Ac-SDKP partially or completely prevented these effects. We conclude that Ac-SDKP prevents Gal-3-induced cardiac inflammation, fibrosis, hypertrophy, and dysfunction, possibly via inhibition of the TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antifibrotic effect of Ac-SDKP and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in hypertension.J Hypertens. 2004 Mar;22(3):593-603. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200403000-00023. J Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15076166 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline reduces cardiac collagen cross-linking and inflammation in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats.Clin Sci (Lond). 2014 Jan 1;126(1):85-94. doi: 10.1042/CS20120619. Clin Sci (Lond). 2014. PMID: 23834332 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline on left ventricular collagen deposition in rats with 2-kidney, 1-clip hypertension.Circulation. 2001 Jun 26;103(25):3136-41. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.25.3136. Circulation. 2001. PMID: 11425781 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of thymosin-beta4 and its derivative N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (Ac-SDKP) in cardiac healing after infarction.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2006;6(5):305-11. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200606050-00003. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2006. PMID: 17083265 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Oct;51(4):600-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.10.033. Epub 2010 Nov 6. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21059352 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New and emerging biomarkers in left ventricular systolic dysfunction--insight into dilated cardiomyopathy.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013 Aug;6(4):516-27. doi: 10.1007/s12265-013-9462-3. Epub 2013 Apr 23. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23609585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Tβ4-POP-Ac-SDKP Axis in Organ Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 31;23(21):13282. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113282. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galectin-3, cardiac structure and function, and long-term mortality in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail. 2010 Aug;12(8):826-32. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfq091. Epub 2010 Jun 5. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010. PMID: 20525986 Free PMC article.
-
Tβ4-Ac-SDKP pathway: Any relevance for the cardiovascular system?Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019 Jul;97(7):589-599. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2018-0570. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30854877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Galectin in Cardiovascular Conditions including Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;16(7):978. doi: 10.3390/ph16070978. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37513890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad N, Gabius HJ, Andre S, Kaltner H, Sabesan S, Roy R, Liu B, Macaluso F, Brewer CF. Galectin-3 precipitates as a pentamer with synthetic multivalent carbohydrates and forms heterogeneous cross-linked complexes. J Biol Chem 279: 10841–10847, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Andre S, Unverzagt C, Kojima S, Frank M, Seifert J, Fink C, Kayser K, von der Lieth CW, Gabius HJ. Determination of modulation of ligand properties of synthetic complex-type biantennary N-glycans by introduction of bisecting GlcNAc in silico, in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Biochem 271: 118–134, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Balakumar P, Singh AP, Ganti SS, Krishan P, Ramasamy S, Singh M. Resident cardiac mast cells: are they the major culprit in the pathogenesis of cardiac hypertrophy? Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 102: 5–9, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Belvisi L, Bernardi A, Colombo M, Manzoni L, Potenza D, Scolastico C, Giannini G, Marcellini M, Riccioni T, Castorina M, Logiudice P, Pisano C. Targeting integrins: insights into structure and activity of cyclic RGD pentapeptide mimics containing azabicycloalkane amino acids. Bioorg Med Chem 14: 169–180, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

