Protein kinase Cbeta is a critical regulator of dopamine transporter trafficking and regulates the behavioral response to amphetamine in mice
- PMID: 19098163
- PMCID: PMC2682265
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.108.147959
Protein kinase Cbeta is a critical regulator of dopamine transporter trafficking and regulates the behavioral response to amphetamine in mice
Abstract
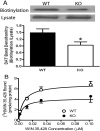
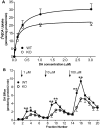
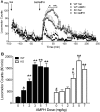
The dopamine transporter (DAT) is a key mediator of dopaminergic neurotransmission and a major target for amphetamine. We found previously that protein kinase C (PKC) beta regulates amphetamine-mediated dopamine efflux. Here, using PKCbeta wild-type (WT) and knockout (KO) mice, we report a novel role for PKCbeta in amphetamine-induced regulation of DAT trafficking and activity. PKCbeta KO mice have less striatal surface DAT, [3H]dopamine uptake, and amphetamine-stimulated dopamine efflux, yet higher novelty-induced locomotor activity than WT mice. Although a short exposure (< or =90 s) to amphetamine rapidly increases striatal surface DAT and [3H]dopamine uptake in WT mice, this treatment decreases surface DAT and [3H]dopamine uptake in KO mice. Increases in surface DAT and [3H]dopamine uptake are not evident in KO mice until a longer exposure (60 min) to amphetamine, by which time WT mice exhibit decreased surface DAT and dopamine uptake. The slowness of amphetamine-induced striatal DAT trafficking in PKCbeta KO mice was mimicked by the use of a specific PKCbeta inhibitor, LY379196, in WT mice. Furthermore, PKCbeta KO mice exhibit reduced locomotor responsiveness to amphetamine compared with WT, which could be explained by reduced surface DAT and delayed amphetamine-induced DAT trafficking in KO mice. Our results indicate that PKCbeta is crucial for proper trafficking of DAT to the surface and for functioning of DAT and amphetamine signaling, providing new insight into the role of PKCbeta as an important regulator of dopaminergic homeostasis.
Figures



References
-
- Blobe GC, Stribling DS, Fabbro D, Stabel S, and Hannun YA (1996) Protein kinase C beta II specifically binds to and is activated by F-actin. J Biol Chem 271 15823-15830. - PubMed
-
- Bolan EA, Kivell B, Jaligam V, Oz M, Jayanthi LD, Han Y, Sen N, Urizar E, Gomes I, Devi LA, et al. (2007) D2 receptors regulate dopamine transporter function via an extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2-dependent and phosphoinositide 3 kinase-independent mechanism. Mol Pharmacol 71 1222-1232. - PubMed
-
- Browman KE, Kantor L, Richardson S, Badiani A, Robinson TE, and Gnegy ME (1998) Injection of the protein kinase C inhibitor Ro31-8220 into the nucleus accumbens attenuates the acute response to amphetamine: tissue and behavioral studies. Brain Res 814 112-119. - PubMed
-
- Cervinski MA, Foster JD, and Vaughan RA (2005) Psychoactive substrates stimulate dopamine transporter phosphorylation and down-regulation by cocaine-sensitive and protein kinase C-dependent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 280 40442-40449. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

