Gamma-secretase inhibitors reverse glucocorticoid resistance in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 19098907
- PMCID: PMC2692090
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1900
Gamma-secretase inhibitors reverse glucocorticoid resistance in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
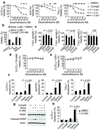
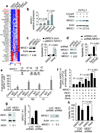
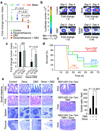
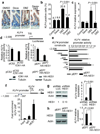
Gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSIs) block the activation of the oncogenic protein Notch homolog-1 (NOTCH1) in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). However, limited antileukemic cytotoxicity and severe gastrointestinal toxicity have restricted the clinical application of these targeted drugs. Here we show that combination therapy with GSIs plus glucocorticoids can improve the antileukemic effects of GSIs and reduce their gut toxicity in vivo. Inhibition of NOTCH1 signaling in glucocorticoid-resistant T-ALL restored glucocorticoid receptor autoupregulation and induced apoptotic cell death through induction of the gene encoding BCL-2-like apoptosis initiator-11 (BCL2L11). GSI treatment resulted in cell cycle arrest and accumulation of goblet cells in the gut mediated by upregulation of the gene encoding the transcription factor Krüppel-like factor-4 (Klf4), a negative regulator of the cell cycle required for goblet cell differentiation. In contrast, glucocorticoid treatment induced transcriptional upregulation of cyclin D2 (Ccnd2) and protected mice from developing the intestinal goblet cell metaplasia typically induced by inhibition of NOTCH signaling with GSIs. These results support a role for glucocorticoids plus GSIs in the treatment of glucocorticoid-resistant T-ALL.
Figures

Comment in
-
Gamma-secretase inhibitors: Notch so bad.Nat Med. 2009 Jan;15(1):20-1. doi: 10.1038/nm0109-20. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19129776 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: NOTCHing the way toward a better treatment outcome.Cancer Cell. 2009 Feb 3;15(2):85-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.01.007. Cancer Cell. 2009. PMID: 19185842
References
-
- Evin G, Sernee MF, Masters CL. Inhibition of gamma-secretase as a therapeutic intervention for Alzheimer's disease: prospects, limitations and strategies. CNS Drugs. 2006;20:351–372. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe D, Kopan R. Notch and Presenilin: regulated intramembrane proteolysis links development and degeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:565–597. - PubMed
-
- Weng AP, et al. Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science. 2004;306:269–271. - PubMed
-
- Roy M, Pear WS, Aster JC. The multifaceted role of Notch in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Deangelo D, et al. A phase I clinical trial of the notch inhibitor MK-0752 in patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (T-ALL) and other leukemias. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2006 ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings Part I. 2006;24:6585.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

