Dcx reexpression reduces subcortical band heterotopia and seizure threshold in an animal model of neuronal migration disorder
- PMID: 19098909
- PMCID: PMC2715867
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1897
Dcx reexpression reduces subcortical band heterotopia and seizure threshold in an animal model of neuronal migration disorder
Erratum in
- Nat Med. 2011 Nov;17(11):1521
Abstract
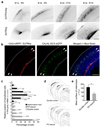
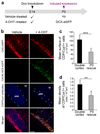
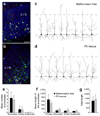
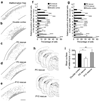
Disorders of neuronal migration can lead to malformations of the cerebral neocortex that greatly increase the risk of seizures. It remains untested whether malformations caused by disorders in neuronal migration can be reduced by reactivating cellular migration and whether such repair can decrease seizure risk. Here we show, in a rat model of subcortical band heterotopia (SBH) generated by in utero RNA interference of the Dcx gene, that aberrantly positioned neurons can be stimulated to migrate by reexpressing Dcx after birth. Restarting migration in this way both reduces neocortical malformations and restores neuronal patterning. We further find that the capacity to reduce SBH continues into early postnatal development. Moreover, intervention after birth reduces the convulsant-induced seizure threshold to a level similar to that in malformation-free controls. These results suggest that disorders of neuronal migration may be eventually treatable by reengaging developmental programs both to reduce the size of cortical malformations and to reduce seizure risk.
Figures


Comment in
-
Moving neurons back into place.Nat Med. 2009 Jan;15(1):17-8. doi: 10.1038/nm0109-17. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19129774 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Normotopic cortex is the major contributor to epilepsy in experimental double cortex.Ann Neurol. 2014 Sep;76(3):428-42. doi: 10.1002/ana.24237. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Ann Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25074818
-
Spared cognitive and behavioral functions prior to epilepsy onset in a rat model of subcortical band heterotopia.Brain Res. 2019 May 15;1711:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.01.030. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30689978
-
Mosaic DCX deletion causes subcortical band heterotopia in males.Neurogenetics. 2012 Nov;13(4):367-73. doi: 10.1007/s10048-012-0339-4. Epub 2012 Jul 26. Neurogenetics. 2012. PMID: 22833188
-
The doublecortin gene family and disorders of neuronal structure.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010 Mar;10(1):32-46. doi: 10.2174/187152410790780118. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20236041 Review.
-
Molecular genetics of neuronal migration disorders.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011 Apr;11(2):171-8. doi: 10.1007/s11910-010-0176-5. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011. PMID: 21222180 Review.
Cited by
-
LIS1 and DCX: Implications for Brain Development and Human Disease in Relation to Microtubules.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:393975. doi: 10.1155/2013/393975. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 24278775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Off-target effect of doublecortin family shRNA on neuronal migration associated with endogenous microRNA dysregulation.Neuron. 2014 Jun 18;82(6):1255-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.036. Neuron. 2014. PMID: 24945770 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal Molecular Approach of in utero Electroporation to Functionally Decipher Endophenotypes in Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Front Mol Neurosci. 2011 Nov 1;4:37. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00037. eCollection 2011. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22065947 Free PMC article.
-
5-aminolevulinic acid, fluorescein sodium, and indocyanine green for glioma margin detection: analysis of operating wide-field and confocal microscopy in glioma models of various grades.Front Oncol. 2023 May 23;13:1156812. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1156812. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37287908 Free PMC article.
-
Basic mechanisms of MCD in animal models.Epileptic Disord. 2009 Sep;11(3):206-14. doi: 10.1684/epd.2009.0273. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Epileptic Disord. 2009. PMID: 19740719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jacobs KM, Kharazia VN, Prince DA. Mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis in cortical malformations. Epilepsy Res. 1999;36:165–188. - PubMed
-
- Chevassus-au-Louis N, Baraban SC, Gaïarsa JL, Ben-Ari Y. Cortical malformations and epilepsy: new insights from animal models. Epilepsia. 1999;40:811–821. - PubMed
-
- Schwartzkroin PA, Walsh CA. Cortical malformations and epilepsy. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2000;6:268–280. - PubMed
-
- Kuzniecky RI, Barkovich AJ. Malformations of cortical development and epilepsy. Brain Dev. 2001;23:2–11. - PubMed
-
- Sisodiya SM. Malformations of cortical development: burdens and insights from important causes of human epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3:29–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

