The growth and tumor suppressors NORE1A and RASSF1A are targets for calpain-mediated proteolysis
- PMID: 19098985
- PMCID: PMC2602596
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003997
The growth and tumor suppressors NORE1A and RASSF1A are targets for calpain-mediated proteolysis
Abstract
Background: NORE1A and RASSF1A are growth and tumour suppressors inactivated in a variety of cancers. Methylation of NORE1A and RASSF1A promoters is the predominant mechanism for downregulation of these proteins; however, other mechanisms are likely to exist.
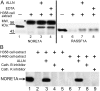
Methodology/principal findings: Here we describe a proteolysis of NORE1A and RASSF1A by calpains as alternative mechanism of their downregulation. Extracts of H358 cell line, a human bronchoalveolar carcinoma, and H460, a large cell carcinoma, were capable of proteolysis of NORE1A protein in the calpain-dependent manner. Likewise, RASSF1A tumor suppressor was proteolyzed by the H358 cell extract. Addition of calpain inhibitor to H358 and H460 cells growing in tissue culture resulted in re-expression of endogenous NORE1A. A survey of 10 human lung tumours revealed that three of them contain an activity capable of inducing NORE1A degradation.
Conclusions/significance: Thus, degradation by calpains is a novel mechanism for downregulation of NORE1A and RASSF1A proteins and might be the mechanism allowing cancer cells to escape growth suppression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of the NORE1A tumor suppressor in Oncogene-Induced Senescence.Cancer Lett. 2017 Aug 1;400:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.030. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28455242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Ras effectors NORE1A and RASSF1A are frequently inactivated in pheochromocytoma and abdominal paraganglioma.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007 Mar;14(1):125-34. doi: 10.1677/ERC-06-0031. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17395981
-
NORE1A tumor suppressor candidate modulates p21CIP1 via p53.Cancer Res. 2009 Jun 1;69(11):4629-37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3672. Epub 2009 May 12. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19435914 Free PMC article.
-
RASSF1A and NORE1A methylation and BRAFV600E mutations in thyroid tumors.Lab Invest. 2005 Sep;85(9):1065-75. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700306. Lab Invest. 2005. PMID: 15980887
-
The RASSF1A tumor suppressor.J Cell Sci. 2007 Sep 15;120(Pt 18):3163-72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.010389. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17878233 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role and Function of Ras-association domain family in Cancer: A Review.Genes Dis. 2019 Jul 27;6(4):378-384. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.07.008. eCollection 2019 Dec. Genes Dis. 2019. PMID: 31832517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RASSF2 associates with and stabilizes the proapoptotic kinase MST2.Oncogene. 2009 Aug 20;28(33):2988-98. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.152. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19525978 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the NORE1A tumor suppressor in Oncogene-Induced Senescence.Cancer Lett. 2017 Aug 1;400:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.030. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28455242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calpain3 is expressed in a proteolitically active form in papillomavirus-associated urothelial tumors of the urinary bladder in cattle.PLoS One. 2010 Apr 22;5(4):e10299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010299. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20421977 Free PMC article.
-
Nonstructural protein 5B promotes degradation of the NORE1A tumor suppressor to facilitate hepatitis C virus replication.Hepatology. 2017 May;65(5):1462-1477. doi: 10.1002/hep.29049. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28090674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vavvas D, Li X, Avruch J, Zhang XF. Identification of Nore1 as a potential Ras effector. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5439–5442. - PubMed
-
- Hesson L, Dallol A, Minna JD, Maher ER, Latif F. NORE1A, a homologue of RASSF1A tumour suppressor gene is inactivated in human cancers. Oncogene. 2003;22:947–954. - PubMed
-
- Tommasi S, Dammann R, Jin SG, Zhang XF, Avruch J, et al. RASSF3 and NORE1: identification and cloning of two human homologues of the putative tumor suppressor gene RASSF1. Oncogene. 2002;21:2713–2720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

