C. elegans RNA-binding proteins PUF-8 and MEX-3 function redundantly to promote germline stem cell mitosis
- PMID: 19100255
- PMCID: PMC2680957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.11.024
C. elegans RNA-binding proteins PUF-8 and MEX-3 function redundantly to promote germline stem cell mitosis
Abstract
Maintenance of mitotically cycling germline stem cells (GSCs) is vital for continuous production of gametes. In worms and insects, signaling from surrounding somatic cells play an essential role in the maintenance of GSCs by preventing premature differentiation. In addition, germ cell proteins such as the Drosophila Pumilio and Caenorhabditis elegans FBF, both members of the PUF family translational regulators, contribute to GSC maintenance. FBF functions by suppressing GLD-1, which promotes meiotic entry. However, factors that directly promote GSC proliferation, rather than prevent differentiation, are not known. Here we show that PUF-8, another C. elegans member of the PUF family and MEX-3, a KH domain translational regulator, function redundantly to promote GSC mitosis. We find that PUF-8 protein is highly enriched in mitotic germ cells, which is similar to the expression pattern of MEX-3 described earlier. The puf-8(-) mex-3(-) double mutant gonads contain far fewer germ cells than both single mutants and wild-type. While these cells lack mitotic, meiotic and sperm markers, they retain the germ cell-specific P granules, and are capable of gametogenesis if GLP-1, which normally blocks meiotic entry, is removed. Significantly, we find that at least one of these two proteins is essential for germ cell proliferation even in meiotic entry-defective mutants, which otherwise produce germ cell tumors. We conclude PUF-8 and MEX-3 contribute to GSC maintenance by promoting mitotic proliferation rather than by blocking meiotic entry.
Figures
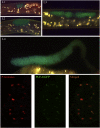
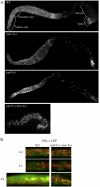
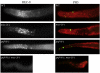
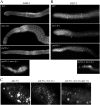
References
-
- Ashcroft N., Golden A. CDC-25.1 regulates germline proliferation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genesis. 2002;33:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Austin J., Kimble J. glp-1 is required in the germ line for regulation of the decision between mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans. Cell. 1987;51:589–599. - PubMed
-
- Berry L.W., Westlund B., Schedl T. Germ-line tumor formation caused by activation of glp-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans member of the Notch family of receptors. Development. 1997;124:925–936. - PubMed
-
- Boxem M., Srinivasan D.G., van den Heuvel S. The Caenorhabditis elegans gene ncc-1 encodes a cdc2-related kinase required for M phase in meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, but not for S phase. Development. 1999;126:2227–2239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

