A highly sensitive and dynamic immunofluorescent cytometric bead assay for the detection of HIV-1 p24
- PMID: 19100289
- PMCID: PMC4154487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2008.11.013
A highly sensitive and dynamic immunofluorescent cytometric bead assay for the detection of HIV-1 p24
Abstract
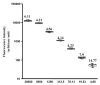
Nucleic acid measurements are used to follow HIV-1 viral load in clinical applications while p24 ELISA is commonly used to monitor HIV-1 replication in research settings. Current ELISA assays are expensive and offer a narrow dynamic measurement range. This report describes a simple, sensitive and inexpensive bead-based assay offering a wide dynamic measurement range. This cytometric bead assay allows the detection of p24 concentrations over 4 orders of magnitude from less than 0.4pg to up to 20,000pgml(-1) in a volume of 50microl and can be combined with other measurements.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Standardization of a cytometric p24-capture bead-assay for the detection of main HIV-1 subtypes.J Virol Methods. 2016 Apr;230:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.01.009. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 26808359 Free PMC article.
-
Proof of principle: an HIV p24 microsphere immunoassay with potential application to HIV clinical diagnosis.Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2009 May;76(3):231-6. doi: 10.1002/cyto.b.20466. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2009. PMID: 19012321
-
Development of a flow cytometric assay for the detection and measurement of neutralizing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus.New Microbiol. 1994 Jan;17(1):21-8. New Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8127226
-
Measurement of HIV-1 p24 antigen by signal-amplification-boosted ELISA of heat-denatured plasma is a simple and inexpensive alternative to tests for viral RNA.AIDS Rev. 2002 Apr-Jun;4(2):83-92. AIDS Rev. 2002. PMID: 12152521 Review.
-
More reliable diagnosis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) by detection of antibody IgGs to pol and gag proteins of HIV-1 and p24 antigen of HIV-1 in urine, saliva, and/or serum with highly sensitive and specific enzyme immunoassay (immune complex transfer enzyme immunoassay): a review.J Clin Lab Anal. 1997;11(5):267-86. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2825(1997)11:5<267::AID-JCLA5>3.0.CO;2-4. J Clin Lab Anal. 1997. PMID: 9292394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles Generated by Gram-Positive Bacteria Protect Human Tissues Ex Vivo From HIV-1 Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 25;11:822882. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.822882. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35145925 Free PMC article.
-
Seminal plasma induces inflammation and enhances HIV-1 replication in human cervical tissue explants.PLoS Pathog. 2017 May 19;13(5):e1006402. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006402. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28542587 Free PMC article.
-
An Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for HIV p24 Based on Fe₃O₄@SiO₂ Nanomagnetic Probes and Nanogold Colloid-Labeled Enzyme-Antibody Copolymer as Signal Tag.Materials (Basel). 2013 Mar 25;6(4):1255-1269. doi: 10.3390/ma6041255. Materials (Basel). 2013. PMID: 28809208 Free PMC article.
-
Productive HIV-1 infection of human cervical tissue ex vivo is associated with the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle.Mucosal Immunol. 2013 Nov;6(6):1081-90. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.2. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Mucosal Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23385427 Free PMC article.
-
An ex vivo Model of HIV-1 Infection in Human Lymphoid Tissue and Cervico-vaginal Tissue.Bio Protoc. 2014;4(4):e1047. doi: 10.21769/bioprotoc.1047. Bio Protoc. 2014. PMID: 25774380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boni J, Opravil M, Omasik Z, Rothen M, Bisset L, Grob PJ, Luthy R, Schupbach J. Simple monitoring of antiretroviral therapy with a signal-amplification-boosted HIV-1 p24 antigen assay with heat-denatured plasma. AIDS. 1997;11:F47–52. - PubMed
-
- Brunstein J, Thomas E. Direct screening of clinical specimens for multiple respiratory pathogens using the Genaco respiratory panels 1 and 2. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2006;15:169–173. - PubMed
-
- Faucher S, Martel A, Sherring A, Ding T, Malloch L, Kim JE, Bergeron M, Sandstrom P, Mandy FF. Protein bead array for the detection of HIV-1 antibodies from fresh plasma and dried-blood-spot specimens. Clin. Chem. 2004;50:1250–1253. - PubMed
-
- Fiscus SA, Pilcher CD, Miller WC, Powers KA, Hoffman IF, Price M, Chilongozi DA, Mapanje C, Krysiak R, Gama S, Martinson FE, Cohen MS. Rapid, real-time detection of acute HIV infection in patients in Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2007;195:416–424. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

