Extract of the Chinese herbal formula Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan inhibited adjuvant arthritis in rats
- PMID: 19100323
- PMCID: PMC2818782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.11.018
Extract of the Chinese herbal formula Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan inhibited adjuvant arthritis in rats
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: The herbal formula Huo Luo Xiao Ling Dan (HLXL) and its modifications have been used in traditional Chinese medicine for about one hundred years to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Aim: To investigate the effects of HLXL on complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced multiple-joint arthritis in rats.
Materials and methods: Male Lewis rats, 190-210 g, were immunized subcutaneously at the base of the tail with 200 microl of heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mineral oil (5 mg/ml). HLXL (2.30 and 4.60 g/kg) or vehicle control (n=8 per group) was administered orally (i.g.) once a day between days 16 and 25 post-CFA injection. The rats were observed for signs of arthritis with arthritic changes (erythema, edema, induration) being scored on a scale of 0-4 of increasing severity using a standard scoring system. The maximum arthritis score per rat was 16. A plethysmometer was used to measure edema volume in each paw. Adverse effects of HLXL were monitored by closely observing the animals for unusual behavioral changes. Levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta) in local tissue were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay on day 25 post-CFA.
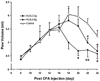
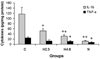
Results: HLXL significantly decreased arthritis scores between days 23-25 in the 2.30 g/kg group and 21-25 in the 4.60 g/kg group (p<0.05). It reduced paw edema on days 22 and 24 in the 2.30 g/kg group and on days 20, 22 and 24 in the 4.60 g/kg group compared to control (p<0.05). Local tissue TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels on day 25 post-CFA injection were significantly (p<0.05) lower in rats treated with HLXL than in control rats. No observable adverse effects were found.
Conclusion: The data suggest that HLXL produces significant anti-arthritic effects that may be mediated by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines, and it appears to be safe.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes PM, Powell-Griner E, McFann K, Nahin RL. Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use Among Adults: United States, 2002. Advance Data From Vital and Health Statistics. 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bensky D, Barolet R. Chinese herbal medicine: Formulas & Strategies. Seattle: Eastland Press; 1990.
-
- Bensky D, Gamble A. Chinese Herbal Medicine: Materia Medica. revised edition. Seattle, Washington: Eastland Press; 1993.
-
- Chandrashekara S, Anilkumar T, Jamuna S. Complementary and alternative drug therapy in arthritis. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India. 2002;50:225–227. - PubMed
-
- China State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The Guidelines for Developing New Chinese Herbal Medicine. Beijing: 1999. Testing Guidelines for Safety Evaluation of New Drug.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

