A KIT juxtamembrane PY567 -directed pathway provides nonredundant signals for erythroid progenitor cell development and stress erythropoiesis
- PMID: 19100679
- PMCID: PMC2701661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.10.009
A KIT juxtamembrane PY567 -directed pathway provides nonredundant signals for erythroid progenitor cell development and stress erythropoiesis
Abstract
Objective: KITL/KIT can elicit diverse sets of signals within lymphoid, myeloid, mast, and erythroid lineages, and exert distinct effects on growth, survival, migration, adhesion, and secretory responses. Presently, we have applied a PY-mutant allele knockin approach to specifically assess possible roles for KIT-PY567 and KIT-PY719 sites, and coupled pathways, during erythropoiesis.
Materials and methods: Mouse models used to investigate this problem include those harboring knocked-in KIT(Y567F/Y567F), KIT(Y569F/Y569F), KIT(Y719F,Y719F), and KIT(Y567F/Y567F:Y569F/Y569F) alleles. The erythron was stressed by myelosuppression using 5-fluorouracil, and by phenylhydrazine-induced hemolysis. In addition, optimized systems for ex vivo analyses of bone marrow and splenic erythropoiesis were employed to more directly analyze possible stage-specific effects on erythroid cell growth, survival, development and KIT signaling events.
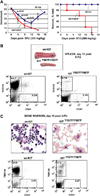
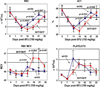
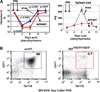
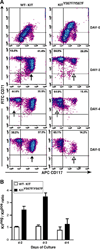
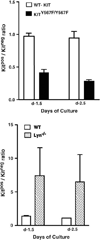
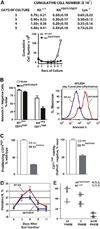
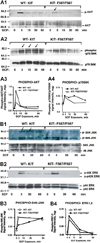
Results: In Kit(Y567F/Y567F) mice, steady-state erythropoiesis was unperturbed while recovery from anemia due to 5-fluorouracil or phenylhydrazine was markedly impaired. Deficiencies in erythroid progenitor expansion occurred both in the bone marrow and the spleen. Responses to chronic erythropoietin dosing were also compromised. Ex vivo, Kit(Y567F/Y567F) (pro)erythroblast development was skewed from a Kit(pos)CD71(high) stage toward a subsequent Kit(neg)CD71(high) compartment. Proliferation and, to an extent, survival capacities were also compromised. Similar stage-specific defects existed for erythroid progenitors from Kit(Y567F/Y567F:Y569F/Y569F) but not KIT(Y719F/Y719F) mice. Kit(Y567F/Y567F) erythroblasts were used further to analyze KIT-PY567-dependent signals. MEK-1,2/ERK-1,2 signaling was unaffected while AKT, p70S6K, and especially JNK2/p54 pathways were selectively attenuated.
Conclusions: Nonredundant KIT-PY567-directed erythroblast-intrinsic signals are selectively critical for stress erythropoiesis. Investigations also add to an understanding of how KIT directs distinct outcomes among diverse progenitors and lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests or conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Podocalyxin selectively marks erythroid-committed progenitors during anemic stress but is dispensable for efficient recovery.Exp Hematol. 2009 Jan;37(1):10-8. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.09.006. Epub 2008 Nov 11. Exp Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19004540
-
Signals for stress erythropoiesis are integrated via an erythropoietin receptor-phosphotyrosine-343-Stat5 axis.J Clin Invest. 2006 Mar;116(3):683-94. doi: 10.1172/JCI25227. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16511603 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of stem cell factor and its receptor c-kit mediates lodgment and acute expansion of hematopoietic cells in the murine spleen.Blood. 1996 Jul 1;88(1):75-81. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8704204
-
Control of erythropoiesis by erythropoietin and stem cell factor: a novel role for Bruton's tyrosine kinase.Cell Cycle. 2004 Jul;3(7):876-9. Epub 2004 Jul 2. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15254422 Review.
-
Role of c-Kit and erythropoietin receptor in erythropoiesis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005 Apr;54(1):63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2004.11.005. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15780908 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential role for focal adhesion kinase in regulating stress hematopoiesis.Blood. 2010 Nov 18;116(20):4103-15. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-262790. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20664055 Free PMC article.
-
GATA Factor-Regulated Samd14 Enhancer Confers Red Blood Cell Regeneration and Survival in Severe Anemia.Dev Cell. 2017 Aug 7;42(3):213-225.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.07.009. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28787589 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved threonine residue in the juxtamembrane domain of the XA21 pattern recognition receptor is critical for kinase autophosphorylation and XA21-mediated immunity.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 2;285(14):10454-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.093427. Epub 2010 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20118235 Free PMC article.
-
Direct engagement of the PI3K pathway by mutant KIT dominates oncogenic signaling in gastrointestinal stromal tumor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 3;114(40):E8448-E8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711449114. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28923937 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of the glucocorticoid receptor in human erythroblasts is uniquely regulated by KIT ligand: implications for stress erythropoiesis.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Oct 10;21(15):2852-65. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0676. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22533504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Richmond TD, Chohan M, Barber DL. Turning cells red: signal transduction mediated by erythropoietin. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:146–155. - PubMed
-
- Munugalavadla V, Kapur R. Role of c-Kit and erythropoietin receptor in erythropoiesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005;54:63–75. - PubMed
-
- Wu H, Liu X, Jaenisch R, Lodish HF. Generation of committed erythroid BFU-E and CFU-E progenitors does not require erythropoietin or the erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1995;83:59–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

