Activation of nociceptin opioid peptide (NOP) receptor impairs contextual fear learning in mice through glutamatergic mechanisms
- PMID: 19100850
- PMCID: PMC4482120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2008.12.001
Activation of nociceptin opioid peptide (NOP) receptor impairs contextual fear learning in mice through glutamatergic mechanisms
Abstract
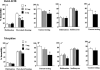
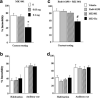
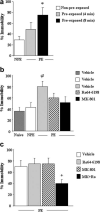
The present study investigated whether the selective nociceptin opioid peptide (NOP) receptor agonist, Ro64-6198, impairs acquisition of fear conditioning through glutamatergic mechanisms. Systemic administration of Ro64-6198 (0.3 and 1mg/kg) or the non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, MK-801 (0.03 and 0.1mg/kg) prior to conditioning severely impaired contextual but not cued fear learning in C57BL/6N mice. When administered together at sub-effective doses, Ro64-6198 (0.5mg/kg) and MK-801 (0.05mg/kg), synergistically impaired contextual fear learning, but left cued fear learning intact. We next used the immediate shock deficit paradigm (ISD) to examine the effects of Ro64-6198 and MK-801 on contextual memory formation in the absence of the foot-shock. As expected, naive mice that were shocked briefly after being placed in the training chamber displayed no contextual fear conditioning. This learning deficit was elevated by prior exposure of mice to the training context. Furthermore, administration of Ro64-6198 and MK-801, either separately at amnesic doses (1mg/kg and 0.1mg/kg, respectively) or concomitantly at sub-effective doses (0.5mg/kg and 0.05mg/kg, respectively) significantly reduced the facilitating effects of context preexposure. These findings demonstrate the existence of functional antagonism between NOP and NMDA receptors that predominantly contributes to modulation of conditioned fear learning which involves spatial-processing demands.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The nociceptin orphanin FQ peptide receptor agonist, Ro64-6198, impairs recognition memory formation through interaction with glutamatergic but not cholinergic receptor antagonists.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Oct;98(3):254-60. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.09.002. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22982481
-
Activation of nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptors inhibits contextual fear memory reconsolidation.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28705439
-
NMDA receptor antagonism disrupts acquisition and retention of the context preexposure facilitation effect in adolescent rats.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Mar 15;301:168-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.12.025. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26711910 Free PMC article.
-
The nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor (NOP) as a target for drug abuse medications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(9):1151-6. doi: 10.2174/156802611795371341. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21050175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of Translationally Informed Treatments for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Animal Models of Pavlovian Fear Conditioning to Human Clinical Trials.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Sep 1;78(5):E15-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jun 15. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26238379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of pronociceptin and its receptor is downregulated in the brain of human alcoholics.Brain Res. 2009 Dec 11;1305 Suppl(Suppl):S80-5. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.05.067. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19501074 Free PMC article.
-
The context preexposure facilitation effect in mice: a dose-response analysis of pretraining scopolamine administration.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Nov 20;225(1):290-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.07.044. Epub 2011 Jul 30. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21827794 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of the role of the nociceptin receptor system in stress, cognition, and reward: relevance to schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 2;8(1):38. doi: 10.1038/s41398-017-0080-8. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29391391 Free PMC article.
-
Further characterization of the prototypical nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptor agonist Ro 64-6198 in rodent models of conflict anxiety and despair.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Jul;222(2):203-14. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2636-x. Epub 2012 Jan 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22249359
References
-
- Ahi J, Radulovic J, Spiess J. The role of hippocampal signaling cascades in consolidation of fear memory. Behavioural Brain Research. 2004;149:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Momose K, Ueno N, Fujino MA, Kasuga M. Endomorphins have orexigenic and anxiolytic activities in mice. Neuroreport. 1998;9:2265–2267. - PubMed
-
- Bardgett ME, Boeckman R, Krochmal D, Fernando H, Ahrens R, Csernansky JG. NMDA receptor blockade and hippocampal neuronal loss impair fear conditioning and position habit reversal in C57Bl/6 mice. Brain Research Bulletin. 2003;60:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Bast T, Zhang WN, Feldon J. Dorsal hippocampus and classical fear conditioning to tone and context in rats: Effects of local NMDA-receptor blockade and stimulation. Hippocampus. 2003;13:657–675. - PubMed
-
- Bolivar VJ, Pooler O, Flaherty L. Inbred strain variation in contextual and cued fear conditioning behavior. Mammalian Genome. 2001;12:651–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

