An evaluation of recollection and familiarity in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment using receiver operating characteristics
- PMID: 19101064
- PMCID: PMC2743328
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandc.2008.11.003
An evaluation of recollection and familiarity in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment using receiver operating characteristics
Abstract
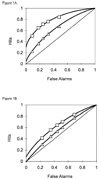
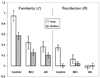
There is a need to investigate exactly how memory breaks down in the course of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Examining what aspects of memorial processing remain relatively intact early in the disease process will allow us to develop behavioral interventions and possible drug therapies focused on these intact processes. Several recent studies have worked to understand the processes of recollection and familiarity in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and very mild AD. Although there is general agreement that these patient groups are relatively unable to use recollection to support veridical recognition decisions, there has been some question as to how well these patients can use familiarity. The current study used receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and a depth of processing manipulation to understand the effect of MCI and AD on the estimates of recollection and familiarity. Results showed that patients with MCI and AD were impaired in both recollection and familiarity, regardless of the depth of encoding. These results are discussed in relation to disease pathology and in the context of recent conflicting evidence as to whether familiarity remains intact in patients with MCI. The authors highlight differences in stimuli type and task difficulty as possibly modulating the ability of these patients to successfully use familiarity in support of memorial decisions.
Figures

References
-
- Adjutant General’s Office. Army Individual Test Battery: Manual of Directions and Scoring. Washington, D.C: War Department; 1944.
-
- Aggleton JP, Vann SD, Denby C, Dix S, Mayes AR, Roberts N, Yonelinas AP. Sparing of the familiarity component of recognition memory in a patient with hippocampal pathology. Neuropsychologia. 2005;43:1810–1823. - PubMed
-
- Allan K, Wilding EL, Rugg MD. Electrophysiological evidence for dissociable processes contributing to recollection. Acta Psychol. 1998;98:231–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

