Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A and protein kinase C phosphorylate alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor subunits at distinct stages of receptor formation and maturation
- PMID: 19101612
- PMCID: PMC2664513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.11.032
Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A and protein kinase C phosphorylate alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor subunits at distinct stages of receptor formation and maturation
Abstract
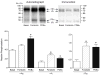
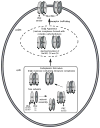
Neuronal nicotinic receptor alpha4 subunits associated with nicotinic alpha4beta2 receptors are phosphorylated by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC), but the stages of receptor formation during which phosphorylation occurs and the functional consequences of kinase activation are unknown. SH-EP1 cells transfected with DNAs coding for human alpha4 and/or beta2 subunits were incubated with (32)Pi, and PKA or PKC was activated by forskolin or phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate, respectively. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting of proteins from cells expressing alpha4beta2 receptors or only alpha4 subunits were used to identify free alpha4 subunits, and alpha4 subunits present in immature alpha4beta2 complexes and mature alpha4beta2 pentamers containing complex carbohydrates. In the absence of kinase activation, phosphorylation of alpha4 subunits associated with mature pentamers was three times higher than subunits associated with immature complexes. PKA and PKC activation increased phosphorylation of free alpha4 subunits on different serine residues; only PKC activation phosphorylated subunits associated with mature alpha4beta2 receptors. Activation of both PKA and PKC increased the density of membrane-associated receptors, but only PKC activation increased peak membrane currents. PKA and PKC activation also phosphorylated beta2 subunits associated with mature alpha4beta2 receptors. Results indicate that activation of PKA and PKC leads to the phosphorylation alpha4beta2 receptors at different stages of receptor formation and maturation and has differential effects on the expression and function of human alpha4beta2 receptors.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nicotine-induced up regulation of α4β2 neuronal nicotinic receptors is mediated by the protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of α4 subunits.Neuroscience. 2010 Nov 24;171(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.09.005. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20837109 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the alpha4 subunit of human alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptors: role of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and protein kinase C (PKC).Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003 May 26;114(1):65-72. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(03)00138-4. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12782394
-
Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylates Ser362 and 467 and protein kinase C phosphorylates Ser550 within the M3/M4 cytoplasmic domain of human nicotinic receptor alpha4 subunits.J Neurochem. 2007 Oct;103(2):456-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04853.x. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17897355
-
Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and protein kinase C phosphorylate sites in the amino acid sequence corresponding to the M3/M4 cytoplasmic domain of alpha4 neuronal nicotinic receptor subunits.J Neurochem. 2001 Feb;76(3):711-20. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00041.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11158241
-
Identification of three cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) phosphorylation sites within the major intracellular domain of neuronal nicotinic receptor alpha4 subunits.J Neurochem. 2002 Jul;82(2):439-47. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2002.01027.x. J Neurochem. 2002. PMID: 12124445
Cited by
-
Effects of nicotine on DARPP-32 and CaMKII signaling relevant to addiction.Adv Pharmacol. 2021;90:89-115. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2020.09.002. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Adv Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33706940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Desformylflustrabromine Modulates α4β2 Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor High- and Low-Sensitivity Isoforms at Allosteric Clefts Containing the β2 Subunit.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Aug;354(2):184-94. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.223933. Epub 2015 May 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 26025967 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Structure and Function and Response to Nicotine.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015;124:3-19. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26472524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic modulation of hippocampal cell signaling and associated effects on learning and memory.Physiol Behav. 2016 Mar 1;155:162-71. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.12.008. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 26687895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotine-induced up regulation of α4β2 neuronal nicotinic receptors is mediated by the protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of α4 subunits.Neuroscience. 2010 Nov 24;171(1):12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.09.005. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20837109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyle WJ, van der Geer P, Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. - PubMed
-
- Darsow T, Booker TK, Piña-Crespo JC, Heinemann SF. Exocytotic trafficking is required for nicotine-induced up-regulation of α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18311–18320. - PubMed
-
- Eaton JB, Peng JH, Schroeder KM, George AA, Fryer JD, Krishnan C, Buhlman L, Kuo YP, Steinlein O, Lukas RJ. Characterization of human α4β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors stably and heterologously expressed in native nicotinic receptor-null SH-EP1 human epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;64:1283–1294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

