Freezing-induced fluid-matrix interaction in poroelastic material
- PMID: 19102561
- PMCID: PMC2703592
- DOI: 10.1115/1.3005170
Freezing-induced fluid-matrix interaction in poroelastic material
Abstract
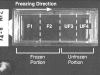
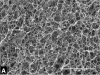
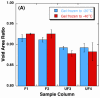
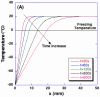
Freezing of biological tissue is emerging in various biomedical applications. The success of these applications requires precise control of the tissue functionality, which is closely associated with the microstructure of the extracellular matrix (ECM). In the present study, the spatiotemporal effects of freezing on the ECM were experimentally and theoretically investigated by approximating biological tissue as a poroelastic material saturated with interstitial fluid. The experiments with type I collagen gel showed that its matrix underwent two distinct levels of structural changes due to freezing: enlarged pore structure of the matrix and increased collagen fibril diameters. The extent of these changes was augmented as the freezing temperature was lowered. The theoretical model suggested that the interstitial fluid might be transported toward the unfrozen region from the phase change interface due to the volumetric expansion associated with the water-ice phase change, and the transported fluid could interact with the matrix and enlarge its pore structure. The model also illustrated the effects of matrix structural properties on this interaction including initial porosity, hydraulic conductivity, and elastic modulus. These results imply that an identical macroscopic freezing protocol may result in different microstructural alterations of poroelastic materials depending on the structural properties of the matrix. This may be relevant to understanding the tissue-type dependent outcomes of cryomedicine applications and be useful in designing cryomedicine applications for a wide variety of tissues.
Figures











References
-
- Rubinsky B. Cryosurgery. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 2000;2:157–187. - PubMed
-
- Kataoka T, Honda Y, Bonneau HN. New Catheter-Based Technology for the Treatment of Restenosis. Journal of Interventional Cardiology. 2002;15(5):371–379. - PubMed
-
- Grassl ED, Bischof JC. In Vitro Model Systems for Evaluation of Smooth Muscle Cell Response to Cryoplasty. Cryobiology. 2005;50(2):162–173. - PubMed
-
- Keane D. New Catheter Ablation Techniques for the Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cardiac Electrophysiology Review. 2002;6(4):341–348. - PubMed
-
- Skanes AC, Yee R, Krahn AD. Cryoablation of Atrial Arrhythmias. Cardiac Electrophysiology Review. 2002;6(4):383–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

