Is intracranial atherosclerosis an independent risk factor for cerebral atrophy? A retrospective evaluation
- PMID: 19102733
- PMCID: PMC2630977
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-8-51
Is intracranial atherosclerosis an independent risk factor for cerebral atrophy? A retrospective evaluation
Abstract
Background: Our purpose was to study the association between the intracranial atherosclerosis as measured by cavernous carotid artery calcification (ICAC) observed on head CT and atrophic changes of supra-tentorial brain demonstrated by MRI.
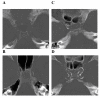
Methods: Institutional review board approval was obtained for this retrospective study incorporating 65 consecutive patients presenting acutely who had both head CT and MRI. Arterial calcifications of the intracranial cavernous carotids (ICAC) were assigned a number (1 to 4) in the bone window images from CT scans. These 4 groups were then combined into high (grades 3 and 4) and low calcium (grades 1 and 2) subgroups. Brain MRI was independently evaluated to identify cortical and central atrophy. Demographics and cardiovascular risk factors were evaluated in subjects with high and low ICAC. Relationship between CT demonstrated ICAC and brain atrophy patterns were evaluated both without and with adjustment for cerebral ischemic scores and cardiovascular risk factors.
Results: Forty-six of the 65 (71%) patients had high ICAC on head CT. Subjects with high ICAC were older, and had higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease (CAD), atrial fibrillation and history of previous stroke (CVA) compared to those with low ICAC. Age demonstrated strong correlation with both supratentorial atrophy patterns. There was no correlation between ICAC and cortical atrophy. There was correlation however between central atrophy and ICAC. This persisted even after adjustment for age.
Conclusion: Age is the most important determinant of atrophic cerebral changes. However, high ICAC demonstrated age independent association with central atrophy.
Figures


References
-
- Brinkman SD, Sarwar M, Levin HS, Morris HH. Quantitative indexes of computed tomography in dementia and normal aging. Radiology. 1981;138:89–92. - PubMed
-
- Ylikoski A, Erkinjuntti T, Raininko R, Sarna S, Sulkava R, Tilvis R. White matter hyperintensities on MRI in the neurologically nondiseased elderly. Analysis of cohorts of consecutive subjects aged 55 to 85 years living at home. Stroke. 1995;26:1171–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

