The effect of antipsychotic medication on sexual function and serum prolactin levels in community-treated schizophrenic patients: results from the Schizophrenia Trial of Aripiprazole (STAR) study (NCT00237913)
- PMID: 19102734
- PMCID: PMC2637262
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-8-95
The effect of antipsychotic medication on sexual function and serum prolactin levels in community-treated schizophrenic patients: results from the Schizophrenia Trial of Aripiprazole (STAR) study (NCT00237913)
Abstract
Background: The aim of this paper is to evaluate the effect of antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia in a community based study on sexual function and prolactin levels comparing the use of aripiprazole and standard of care (SOC), which was a limited choice of three widely used and available antipsychotics (olanzapine, quetiapine or risperidone) (The Schizophrenia Trial of Aripiprazole [STAR] study [NCT00237913]).
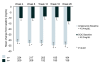
Method: This open-label, 26-week, multi-centre, randomised study compared aripiprazole to SOC (olanzapine, quetiapine or risperidone) in patients with schizophrenia (DSM-IV-TR criteria). The primary effectiveness variable was the mean total score of the Investigator Assessment Questionnaire (IAQ) at Week 26. The outcome research variables included the Arizona Sexual Experience scale (ASEX). This along with the data collected on serum prolactin levels at week 4, 8, 12, 18 and 26 will be the focus of this paper.
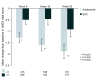
Results: A total of 555 patients were randomised to receive aripiprazole (n = 284) or SOC (n = 271). Both treatment groups experienced improvements in sexual function from baseline ASEX assessments. However at 8 weeks the aripiprazole treatment group reported significantly greater improvement compared with the SOC group (p = 0.007; OC). Although baseline mean serum prolactin levels were similar in the two treatment groups (43.4 mg/dL in the aripiprazole group and 42.3 mg/dL in the SOC group, p = NS) at Week 26 OC, mean decreases in serum prolactin were 34.2 mg/dL in the aripiprazole group, compared with 13.3 mg/dL in the SOC group (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The study findings suggest that aripiprazole has the potential to reduce sexual dysfunction, which in turn might improve patient compliance.
Figures
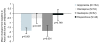

References
-
- Klibanski A, Neer RM, Beitins IZ, et al. Decreased bone density in hyperprolactinemic women. N Engl J Med. 1980;303:1511–1514. - PubMed
-
- Smith S, Gillam A. Sexual dysfunction – the forgotten taboo. Mental Health Nurs. 2005;25:6–9.
-
- Gopalakrishnan R, Jacob KS, Kuruvilla A, Vasantharaj B, John JK. Sildenafil in the Treatment of Antipsychotic-Induced Erectile Dysfunction: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Flexible-Dose, Two-Way Crossover Trial. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:494–499. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.163.3.494. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

