Stimulus-reinforcement-based decision making and anxiety: impairment in generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) but not in generalized social phobia (GSP)
- PMID: 19102795
- PMCID: PMC2999404
- DOI: 10.1017/S003329170800487X
Stimulus-reinforcement-based decision making and anxiety: impairment in generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) but not in generalized social phobia (GSP)
Abstract
Background: Generalized social phobia (GSP) involves the fear/avoidance of social situations whereas generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) involves an intrusive worry about everyday life circumstances. It remains unclear whether these, highly co-morbid, conditions represent distinct disorders or alternative presentations of a single underlying pathology. In this study, we examined stimulus-reinforcement-based decision making in GSP and GAD.
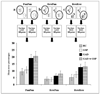
Method: Twenty unmedicated patients with GSP, 16 unmedicated patients with GAD and 19 age-, IQ- and gender-matched healthy comparison (HC) individuals completed the Differential Reward/Punishment Learning Task (DRPLT). In this task, the subject chooses between two objects associated with different levels of reward or punishment. Thus, response choice indexes not only reward/punishment sensitivity but also sensitivity to reward/punishment level according to between-object reinforcement distance.
Results: We found that patients with GAD committed a significantly greater number of errors than both the patients with GSP and the HC individuals. By contrast, the patients with GSP and the HC individuals did not differ in performance on this task.
Conclusions: These results link GAD with anomalous non-affective-based decision making. They also indicate that GSP and GAD are associated with distinct pathophysiologies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures to report.
Figures

References
-
- Becker ES, Rinck M, Margraf J, Roth WT. The emotional Stroop effect in anxiety disorders: general emotional or disorder specificity? Journal of Anxiety Disorders. 2001;15:147–159. - PubMed
-
- Birbaumer N, Grodd W, Diedrich O, Klose U, Erb M, Lotze M, Schneider F, Weiss U, Flor H. fMRI reveals amygdala activation to human faces in social phobics. Neuroreport. 1998;9:1223–1226. - PubMed
-
- Blair KS, Leonard A, Morton J, Blair RJR. Impaired decision making on the basis of both reward and punishment information in individuals with psychopathy. Personality and Individual Differences. 2006a;41:155–165.
-
- Blair KS, Marsh AA, Morton J, Vythilingham M, Jones M, Mondillo K, Pine DS, Drevets WC, Blair RJR. Choosing the lesser of two evils, the better of two goods: Specifying the roles of ventromedial prefrontal cortex and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in object choice. Journal of Neuroscience. 2006b;26:11379–11386. - PMC - PubMed

