Clinical cancer advances 2008: major research advances in cancer treatment, prevention, and screening--a report from the American Society of Clinical Oncology
- PMID: 19103723
- PMCID: PMC2645086
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.2134
Clinical cancer advances 2008: major research advances in cancer treatment, prevention, and screening--a report from the American Society of Clinical Oncology
Erratum in
- J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jun 20;27(18):3070-1
Abstract
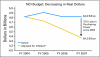
A message from ASCO'S president: Nearly 40 years ago, President Richard Nixon signed the National Cancer Act, mobilizing the country's resources to make the "conquest of cancer a national crusade." That declaration led to a major investment in cancer research that has significantly improved cancer prevention, treatment, and survival. As a result, two thirds of people diagnosed with cancer today will live at least 5 years after diagnosis, compared with just half in the 1970s. In addition, there are now more than 12 million cancer survivors in the United States--up from 3 million in 1971. Scientifically, we have never been in a better position to advance cancer treatment. Basic scientific research, fueled in recent years by the tools of molecular biology, has generated unprecedented knowledge of cancer development. We now understand many of the cellular pathways that can lead to cancer. We have learned how to develop drugs that block those pathways; increasingly, we know how to personalize therapy to the unique genetics of the tumor and the patient. Yet in 2008, 1.4 million people in the United States will still be diagnosed with cancer, and more than half a million will die as a result of the disease. Some cancers remain stubbornly resistant to treatment, whereas others cannot be detected until they are in their advanced, less curable stages. Biologically, the cancer cell is notoriously wily; each time we throw an obstacle in its path, it finds an alternate route that must then be blocked. To translate our growing basic science knowledge into better treatments for patients, a new national commitment to cancer research is urgently needed. However, funding for cancer research has stagnated. The budgets of the National Institutes of Health and the National Cancer Institute have failed to keep pace with inflation, declining up to 13% in real terms since 2004. Tighter budgets reduce incentives to support high-risk research that could have the largest payoffs. The most significant clinical research is conducted increasingly overseas. In addition, talented young physicians in the United States, seeing less opportunity in the field of oncology, are choosing other specialties instead. Although greater investment in research is critical, the need for new therapies is only part of the challenge. Far too many people in the United States lack access to the treatments that already exist, leading to unnecessary suffering and death. Uninsured cancer patients are significantly more likely to die than those with insurance, racial disparities in cancer incidence and mortality remain stark, and even insured patients struggle to keep up with the rapidly rising cost of cancer therapies. As this annual American Society of Clinical Oncology report of the major cancer research advances during the last year demonstrates, we are making important progress against cancer. But sound public policies are essential to accelerate that progress. In 2009, we have an opportunity to reinvest in cancer research, and to support policies that will help ensure that every individual in the United States receives potentially life-saving cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment. Sincerely, Richard L. Schilsky, MD President American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Rummel MJ, Atta J, Welslau M, et al. Bendamustine and rituximab (BR) are effective in the treatment of relapsed or refractory indolent and mantle-cell lymphomas: Long-term follow-up of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(suppl):18S. abstr 8034.
-
- Younes A, Forero-Torres A, Bartlett NL, et al. Objective responses in a phase I dose-escalation study of SGN-35, a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting CD30, in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(suppl):460s. abstr 8526.
-
- Goss PE, Ingle JN, Pater JL, et al. Late extended adjuvant treatment with letrozole improves outcome in women with early-stage breast cancer completing 5 years of tamoxifen. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1948–1955. - PubMed
-
- Muss HB, Tu D, Ingle JN, et al. Efficacy, toxicity and quality of life in older women with early-stage breast cancer treated with letrozole or placebo after 5 years of tamoxifen: NCIC CTG Intergroup Trial MA.17. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1956–1964. - PubMed
-
- Peto R, Davies C. ATLAS (Adjuvant Tamoxifen, Longer Against Shorter): International randomized trial of 10 versus 5 years of adjuvant tamoxifen among 11,500 women preliminary results. the 30th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium; December 13–16, 2007; San Antonio, TX. Presented at.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

