Debio 025, a cyclophilin binding molecule, is highly efficient in clearing hepatitis C virus (HCV) replicon-containing cells when used alone or in combination with specifically targeted antiviral therapy for HCV (STAT-C) inhibitors
- PMID: 19104013
- PMCID: PMC2650540
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00939-08
Debio 025, a cyclophilin binding molecule, is highly efficient in clearing hepatitis C virus (HCV) replicon-containing cells when used alone or in combination with specifically targeted antiviral therapy for HCV (STAT-C) inhibitors
Abstract
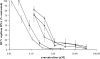
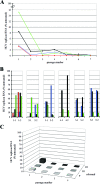
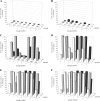
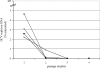
Debio 025 is a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication (J. Paeshuyse et al., Hepatology 43:761-770, 2006). In phase I clinical studies, monotherapy (a Debio 025 dose of 1,200 mg twice a day) resulted in a mean maximal decrease in the viral load of 3.6 log(10) units (R. Flisiak et al., Hepatology 47:817-826, 2008), whereas a reduction of 4.6 log(10) units was obtained in phase II studies when Debio 025 was combined with interferon (R. Flisiak et al., J. Hepatol., 48:S62, 2008). We here report on the particular characteristics of the in vitro anti-HCV activities of Debio 025. The combination of Debio 025 with either ribavirin or specifically targeted antiviral therapy for HCV (STAT-C) inhibitors (NS3 protease or NS5B [nucleoside and nonnucleoside] polymerase inhibitors) resulted in additive antiviral activity in short-term antiviral assays. Debio 025 has the unique ability to clear hepatoma cells from their HCV replicon when it is used alone or in combination with interferon and STAT-C inhibitors. Debio 025, when it was used at concentrations that have been observed in human plasma (0.1 or 0.5 muM), was able to delay or prevent the development of resistance to HCV protease inhibitors as well as to nucleoside and nonnucleoside polymerase inhibitors. Debio 025 forms an attractive drug candidate for the treatment of HCV infections in combination with standard interferon-based treatment and treatments that directly target the HCV polymerase and/or protease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The non-immunosuppressive cyclosporin DEBIO-025 is a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication in vitro.Hepatology. 2006 Apr;43(4):761-70. doi: 10.1002/hep.21102. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16557546
-
Combinations of cyclophilin inhibitor NIM811 with hepatitis C Virus NS3-4A Protease or NS5B polymerase inhibitors enhance antiviral activity and suppress the emergence of resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Sep;52(9):3267-75. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00498-08. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18591281 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of alisporivir plus an NS5A inhibitor provides additive to synergistic anti-hepatitis C virus activity without detectable cross-resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Jun;58(6):3327-34. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00016-14. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24687498 Free PMC article.
-
An evaluation of the cyclophilin inhibitor Debio 025 and its potential as a treatment for chronic hepatitis C.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Feb;18(2):211-20. doi: 10.1517/13543780802651583. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19236267 Review.
-
New HCV therapies on the horizon.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Feb;17(2):122-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03430.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 21087349 Review.
Cited by
-
Fragment-based discovery of a new family of non-peptidic small-molecule cyclophilin inhibitors with potent antiviral activities.Nat Commun. 2016 Sep 22;7:12777. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12777. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27652979 Free PMC article.
-
Curing a viral infection by targeting the host: the example of cyclophilin inhibitors.Antiviral Res. 2013 Jul;99(1):68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23578729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Transcriptomics-Based Bioinformatics Approach for Identification and In Vitro Screening of FDA-Approved Drugs for Repurposing against Dengue Virus-2.Viruses. 2022 Sep 29;14(10):2150. doi: 10.3390/v14102150. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298705 Free PMC article.
-
DEB025 (Alisporivir) inhibits hepatitis C virus replication by preventing a cyclophilin A induced cis-trans isomerisation in domain II of NS5A.PLoS One. 2010 Oct 27;5(10):e13687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013687. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21060866 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclophilin A as a New Therapeutic Target for Hepatitis C Virus-induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;17(5):375-83. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.5.375. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24227937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anonymous. 2008. Pharmasset announces R7128 achieves 85% rapid virologic response in a 4-week combination study for the treatment of chronic hepatitis. Pharmasett, Princeton, NJ. http://investor.pharmasset.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=284920.
-
- Anonymous. 2008. InterMune announces continuing progress on ITMN-191 (R7227). InterMune, Brisbane, CA. http://phx.corporate-ir.net/phoenix.zhtml?c=100067&p=irol-newsArticle&ID....
-
- Anonymous. 2007. Initial results of phase II study with HCV protease inhibitor boceprevir in treatment-naive hepatitis C patients show a high rate of early virologic response. Schering-Plough, Kenilworth, NJ. http://www.schering-plough.com/schering_plough/news/release.jsp?releaseI....
-
- Baba, M., R. Pauwels, J. Balzarini, P. Herdewijn, E. De Clercq, and J. Desmyter. 1987. Ribavirin antagonizes inhibitory effects of pyrimidine 2′,3′-dideoxynucleosides but enhances inhibitory effects of purine 2′,3′-dideoxynucleosides on replication of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31:1613-1617. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

