Structural basis for antagonism of human interleukin 18 by poxvirus interleukin 18-binding protein
- PMID: 19104048
- PMCID: PMC2634891
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809086106
Structural basis for antagonism of human interleukin 18 by poxvirus interleukin 18-binding protein
Abstract
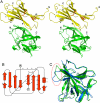
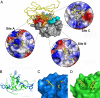
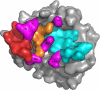
Human interleukin-18 (hIL-18) is a cytokine that plays an important role in inflammation and host defense against microbes. Its activity is regulated in vivo by a naturally occurring antagonist, the human IL-18-binding protein (IL-18BP). Functional homologs of human IL-18BP are encoded by all orthopoxviruses, including variola virus, the causative agent of smallpox. They contribute to virulence by suppressing IL-18-mediated immune responses. Here, we describe the 2.0-A resolution crystal structure of an orthopoxvirus IL-18BP, ectromelia virus IL-18BP (ectvIL-18BP), in complex with hIL-18. The hIL-18 structure in the complex shows significant conformational change at the binding interface compared with the structure of ligand-free hIL-18, indicating that the binding is mediated by an induced-fit mechanism. EctvIL-18BP adopts a canonical Ig fold and interacts via one edge of its beta-sandwich with 3 cavities on the hIL-18 surface through extensive hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions. Most of the ectvIL-18BP residues that participate in these interactions are conserved in both human and viral homologs, explaining their functional equivalence despite limited sequence homology. EctvIL-18BP blocks a putative receptor-binding site on IL-18, thus preventing IL-18 from engaging its receptor. Our structure provides insights into how IL-18BPs modulate hIL-18 activity. The revealed binding interface provides the basis for rational design of inhibitors against orthopoxvirus IL-18BP (for treating orthopoxvirus infection) or hIL-18 (for treating certain inflammatory and autoimmune diseases).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Okamura H, et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-γ production by T cells. Nature. 1995;378:88–91. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Interleukin-18. Methods. 1999;19:121–132. - PubMed
-
- Novick D, et al. Interleukin-18-binding protein: A novel modulator of the Th1 cytokine response. Immunity. 1999;10:127–136. - PubMed
-
- Born TL, et al. A poxvirus protein that binds to and inactivates IL-18 and inhibits NK cell response. J Immunol. 2000;164:3246–3254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

