Neuron network activity scales exponentially with synapse density
- PMID: 19104141
- PMCID: PMC2679226
- DOI: 10.1088/1741-2560/6/1/014001
Neuron network activity scales exponentially with synapse density
Abstract
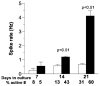
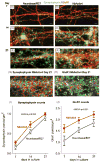
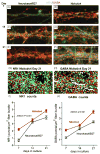
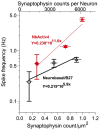
Neuronal network output in the cortex as a function of synapse density during development has not been explicitly determined. Synaptic scaling in cortical brain networks seems to alter excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs to produce a representative rate of synaptic output. Here, we cultured rat hippocampal neurons over a three-week period to correlate synapse density with the increase in spontaneous spiking activity. We followed the network development as synapse formation and spike rate in two serum-free media optimized for either (a) neuron survival (Neurobasal/B27) or (b) spike rate (NbActiv4). We found that while synaptophysin synapse density increased linearly with development, spike rates increased exponentially in developing neuronal networks. Synaptic receptor components NR1, GluR1 and GABA-A also increase linearly but with more excitatory receptors than inhibitory. These results suggest that the brain's information processing capability gains more from increasing connectivity of the processing units than increasing processing units, much as Internet information flow increases much faster than the linear number of nodes and connections.
Figures
References
-
- Barbin G, Pollard H, Gaiarsa JL, Ben Ari Y. Involvement of GABAA receptors in the outgrowth of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1993;152:150–4. - PubMed
-
- Braitenberg V, Schuz A. Cortex: Statistics and Geometry of Neuronal Connectivity. 2. Berlin: Springer; 2004. pp. 19–35.
-
- Brewer GJ, Reichensperger JD, Brinton RD. Prevention of age-related dysregulation of calcium dynamics by estrogen in neurons. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:306–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
