Predicting response to hepatitis C therapy
- PMID: 19104144
- PMCID: PMC2613453
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI38069
Predicting response to hepatitis C therapy
Abstract
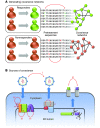
Current treatment for chronic hepatitis C is expensive, is often accompanied by burdensome side effects, and, sadly, fails in almost half of cases. The ability to predict such failures prior to treatment could save a great deal of pain and expense for the patient with HCV. In this issue of the JCI, Aurora and colleagues describe the development of genetic markers predictive of treatment response based on a study of viral sequence variation (see the related article beginning on page 225). Genome-wide covariation analyses of pretreatment virus sequences from 94 patients showed distinct patterns of mutations strongly associated with the ultimate success or failure of treatment. Such analyses suggest markers predictive of response to therapy and may lead to new insights into the underlying biology of hepatitis C.
Figures
Comment on
-
Genome-wide hepatitis C virus amino acid covariance networks can predict response to antiviral therapy in humans.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jan;119(1):225-36. doi: 10.1172/JCI37085. Epub 2008 Dec 22. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19104147 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide hepatitis C virus amino acid covariance networks can predict response to antiviral therapy in humans.J Clin Invest. 2009 Jan;119(1):225-36. doi: 10.1172/JCI37085. Epub 2008 Dec 22. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19104147 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infection].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 1999 Feb;6(32):92-5. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 1999. PMID: 10337182 Review. Polish.
-
Hepatitis C virus diversity and evolution in the full open-reading frame during antiviral therapy.PLoS One. 2008 May 7;3(5):e2123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002123. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18463735 Free PMC article.
-
Can genetic variations predict HCV treatment outcomes?J Hepatol. 2008 Oct;49(4):494-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.07.006. Epub 2008 Jul 21. J Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18692270 No abstract available.
-
Clinical relevance of hepatitis C virus quasispecies.J Viral Hepat. 1995;2(6):267-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.1995.tb00040.x. J Viral Hepat. 1995. PMID: 8732171 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis C virus transmission bottlenecks analyzed by deep sequencing.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(12):6218-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02271-09. Epub 2010 Apr 7. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20375170 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of hepatitis C infections with interferon: a historical perspective.Hepat Res Treat. 2010;2010:323926. doi: 10.1155/2010/323926. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Hepat Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 21152181 Free PMC article.
-
Interferons as Therapy for Viral and Neoplastic Diseases: From Panacea to Pariah to Paragon.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2009 Dec 15;2(3):206-216. doi: 10.3390/ph2030206. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2009. PMID: 27713234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential treatment options and future research to increase hepatitis C virus treatment response rate.Hepat Med. 2010 Oct;2010(2):125-145. doi: 10.2147/HMER.S7193. Hepat Med. 2010. PMID: 21331152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong G.L., et al. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann. Intern. Med. 2006;144:705–714. - PubMed
-
- Torres-Puente M., et al. Genetic variability in hepatitis C virus and its role in antiviral treatment response. J. Viral Hepat. 2008;15:188–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

