MEN epsilon/beta nuclear-retained non-coding RNAs are up-regulated upon muscle differentiation and are essential components of paraspeckles
- PMID: 19106332
- PMCID: PMC2661813
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.087775.108
MEN epsilon/beta nuclear-retained non-coding RNAs are up-regulated upon muscle differentiation and are essential components of paraspeckles
Abstract
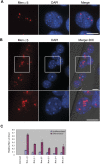
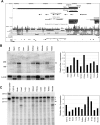
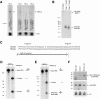
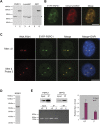
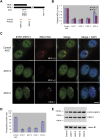
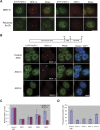
Studies of the transcriptional output of the human and mouse genomes have revealed that there are many more transcripts produced than can be accounted for by predicted protein-coding genes. Using a custom microarray, we have identified 184 non-coding RNAs that exhibit more than twofold up- or down-regulation upon differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts into myotubes. Here, we focus on the Men epsilon/beta locus, which is up-regulated 3.3-fold during differentiation. Two non-coding RNA isoforms are produced from a single RNA polymerase II promoter, differing in the location of their 3' ends. Men epsilon is a 3.2-kb polyadenylated RNA, whereas Men beta is an approximately 20-kb transcript containing a genomically encoded poly(A)-rich tract at its 3'-end. The 3'-end of Men beta is generated by RNase P cleavage. The Men epsilon/beta transcripts are localized to nuclear paraspeckles and directly interact with NONO. Knockdown of MEN epsilon/beta expression results in the disruption of nuclear paraspeckles. Furthermore, the formation of paraspeckles, after release from transcriptional inhibition by DRB treatment, was suppressed in MEN epsilon/beta-depleted cells. Our findings indicate that the MEN epsilon/beta non-coding RNAs are essential structural/organizational components of paraspeckles.
Figures
References
-
- Berezney R., Coffey D.S. Identification of a nuclear protein matrix. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1974;60:1410–1417. - PubMed
-
- Brawerman G., Diez J. Metabolism of the polyadenylate sequence of nuclear RNA and messenger RNA in mammalian cells. Cell. 1975;5:271–280. - PubMed
-
- Bussemakers M.J., van Bokhoven A., Verhaegh G.W., Smit F.P., Karthaus H.F., Schalken J.A., Debruyne F.M., Ru N., Isaacs W.B. DD3: a new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5975–5979. - PubMed
-
- Carninci P., Kasukawa T., Katayama S., Gough J., Frith M.C., Maeda N., Oyama R., Ravasi T., Lenhard B., Wells C., et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005;309:1559–1563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
