Crosstalk between CXCR4/stromal derived factor-1 and VLA-4/VCAM-1 pathways regulates neutrophil retention in the bone marrow
- PMID: 19109194
- PMCID: PMC2633729
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.1.604
Crosstalk between CXCR4/stromal derived factor-1 and VLA-4/VCAM-1 pathways regulates neutrophil retention in the bone marrow
Abstract
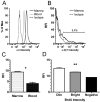
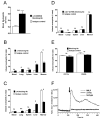
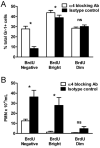
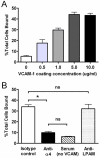
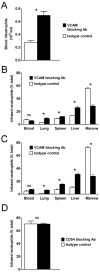
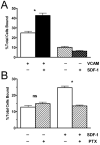
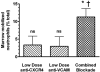
Neutrophil retention in and release from the bone marrow is a critical process that remains incompletely understood. Previous work has implicated the CXCR4/stromal derived factor-1 (SDF-1) chemokine axis in the marrow retention of neutrophils, yet the adhesion pathways responsible for this retention are unknown. Because alpha(4)beta(1) integrin (VLA-4) and its ligand VCAM-1 play a central role in the interactions of hematopoietic stem cells, lymphocytes, and developing neutrophils in the marrow, we investigated whether this integrin might be involved in marrow neutrophil retention and release. In this study, we show that VLA-4 is expressed on murine marrow neutrophils and decreases with maturation, whereas blockade of this integrin leads to the release of marrow neutrophils. Marrow neutrophils adhere via VLA-4 to VCAM-1, which is expressed on marrow endothelium and stroma, and inhibition of VCAM-1 causes release of marrow neutrophils. Furthermore, SDF-1 (CXCL12) signaling through neutrophil CXCR4 augments VLA-4 adhesion to VCAM-1 in vitro, an effect that is blocked by preincubation with pertussis toxin. In vivo blockade of both CXCR4 and alpha(4) causes synergistic release of marrow neutrophils, showing that cross-talk between CXCR4 and VLA-4 modulates marrow retention of these cells. Taken together, these results indicate that the VLA-4/VCAM adhesion pathway is critical in the retention and maturation-controlled release of neutrophils from the marrow, while providing an important link between the CXCR4/SDF-1 signaling axis and the adhesion events that govern this process.
Figures
References
-
- Opdenakker G, Fibbe WE, Van Damme J. The molecular basis of leukocytosis. Immunol Today. 1998;19:182–189. - PubMed
-
- Suratt BT, Petty JM, Young SK, Malcolm KC, Lieber JG, Nick JA, Gonzalo JA, Henson PM, Worthen GS. Role of the CXCR4/SDF-1 chemokine axis in circulating neutrophil homeostasis. Blood. 2004;104:565–571. - PubMed
-
- Ma Q, Jones D, Springer TA. The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is required for the retention of B lineage and granulocytic precursors within the bone marrow microenvironment. Immunity. 1999;10:463–471. - PubMed
-
- Martin C, Burdon PC, Bridger G, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Williams TJ, Rankin SM. Chemokines acting via CXCR2 and CXCR4 control the release of neutrophils from the bone marrow and their return following senescence. Immunity. 2003;19:583–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

