KLF4 gene expression is inhibited by the notch signaling pathway that controls goblet cell differentiation in mouse gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 19109406
- PMCID: PMC2660173
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.90393.2008
KLF4 gene expression is inhibited by the notch signaling pathway that controls goblet cell differentiation in mouse gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
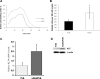
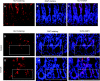
In Kruppel-like factor (KLF)-4-deficient mice, colonic goblet cell numbers are significantly reduced. Goblet cell development is regulated by the Notch signaling pathway. The aim of this study was to examine whether Notch represses KLF4 expression to regulate goblet cell differentiation. We first detected that KLF4 gene expression was upregulated in a human progastrin-overexpressing mouse model where goblet cell hyperplasia has been observed. We then found that mice treated with a gamma-secretase inhibitor (compound E, 10 micromol/kg) for 24 h, which inhibits the Notch signaling pathway, had significantly increased KLF4 mRNA levels in small intestine and colon, accompanied by an increased number of KLF4-expressing cells at the bottom of crypts in small intestine and colon. In a colon cancer cell line (HCT116 cells), KLF4 promoter activity was inhibited by a constitutively active form of Notch1 (ICN1) by transient cotransfection assays. This inhibition was significantly compromised by a dominant-negative RBPjk, a repressive mediator of the Notch signaling pathway. An ICN1-responsive element was then mapped in the human KLF4 promoter between -151 and -122 nucleotides upstream of the transcriptional start site. It was also found that an intact ICN1-responsive element is required for ICN1 to inhibit KLF4 promoter activity by transient cotransfection assays. Our findings thus reveal a possible mechanism by which KLF4 is inhibited by Notch, which controls goblet cell differentiation in mouse gastrointestinal tract.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Notch inhibits expression of the Krüppel-like factor 4 tumor suppressor in the intestinal epithelium.Mol Cancer Res. 2008 Dec;6(12):1920-7. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0224. Mol Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19074836 Free PMC article.
-
Dll1- and dll4-mediated notch signaling are required for homeostasis of intestinal stem cells.Gastroenterology. 2011 Apr;140(4):1230-1240.e1-7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21238454 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish krüppel-like factor 4a represses intestinal cell proliferation and promotes differentiation of intestinal cell lineages.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20974. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020974. Epub 2011 Jun 8. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21687630 Free PMC article.
-
Mastermind-like transcriptional co-activator-mediated Notch signaling is indispensable for maintaining conjunctival epithelial identity.Development. 2013 Feb 1;140(3):594-605. doi: 10.1242/dev.082842. Development. 2013. PMID: 23293291 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial transformation by KLF4 requires Notch1 but not canonical Notch1 signaling.Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Oct;8(19):1840-51. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.19.9440. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19717984 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-Like Factor 4 (KLF4) Is Not Required for Retinal Cell Differentiation.eNeuro. 2016 Feb 27;3(1):ENEURO.0117-15.2016. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0117-15.2016. eCollection 2016 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2016. PMID: 27022622 Free PMC article.
-
Altered intestinal epithelial homeostasis in mice with intestine-specific deletion of the Krüppel-like factor 4 gene.Dev Biol. 2011 Jan 15;349(2):310-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21070761 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical analysis of the γ-secretase inhibitor PF-03084014 in combination with glucocorticoids in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Jul;11(7):1565-75. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0938. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22504949 Free PMC article.
-
Major signaling pathways in intestinal stem cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Feb;1830(2):2410-26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22922290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Potential for NOTCH Targeting?Front Oncol. 2018 Jul 24;8:267. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00267. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30087852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ai W, Liu Y, Langlois M, Wang TC. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) represses histidine decarboxylase gene expression through an upstream Sp1 site and downstream gastrin responsive elements. J Biol Chem 279: 8684–8693, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284: 770–776, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Burgering BM A brief introduction to FOXOlogy. Oncogene 27: 2258–2262, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Crosnier C, Stamataki D, Lewis J. Organizing cell renewal in the intestine: stem cells, signals and combinatorial control. Nat Rev 7: 349–359, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

