Nociceptors are interleukin-1beta sensors
- PMID: 19109489
- PMCID: PMC2690713
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3795-08.2008
Nociceptors are interleukin-1beta sensors
Abstract
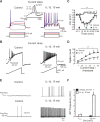
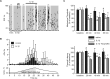
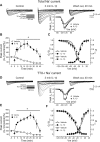
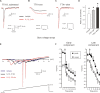
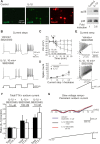
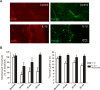
A cardinal feature of inflammation is heightened pain sensitivity at the site of the inflamed tissue. This results from the local release by immune and injured cells of nociceptor sensitizers, including prostaglandin E(2), bradykinin, and nerve growth factor, that reduce the threshold and increase the excitability of the peripheral terminals of nociceptors so that they now respond to innocuous stimuli: the phenomenon of peripheral sensitization. We show here that the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), in addition to producing inflammation and inducing synthesis of several nociceptor sensitizers, also rapidly and directly activates nociceptors to generate action potentials and induce pain hypersensitivity. IL-1beta acts in a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAP kinase)-dependent manner, to increase the excitability of nociceptors by relieving resting slow inactivation of tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channels and also enhances persistent TTX-resistant current near threshold. By acting as an IL-1beta sensor, nociceptors can directly signal the presence of ongoing tissue inflammation.
Figures
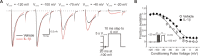
Similar articles
-
The role of slow and persistent TTX-resistant sodium currents in acute tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated increase in nociceptors excitability.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Jan 15;113(2):601-19. doi: 10.1152/jn.00652.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25355965 Free PMC article.
-
Functional tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channels are expressed presynaptically in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 17;159(2):559-69. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.029. Epub 2008 Dec 30. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19162133
-
Analysis of the variation in use-dependent inactivation of high-threshold tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium currents recorded from rat sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 2006 Dec 28;143(4):923-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.052. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 17027172
-
Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in sensory neurons generate slow resurgent currents that are enhanced by inflammatory mediators.J Neurosci. 2014 May 21;34(21):7190-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5011-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24849353 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular signaling in primary sensory neurons and persistent pain.Neurochem Res. 2008 Oct;33(10):1970-8. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9711-z. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 18427980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reciprocal interactions between osteoclasts and nociceptive sensory neurons in bone cancer pain.Pain Rep. 2021 Mar 9;6(1):e867. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000867. eCollection 2021. Pain Rep. 2021. PMID: 33981921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early life programming of pain: focus on neuroimmune to endocrine communication.J Transl Med. 2016 May 6;14(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0879-8. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27154463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1β increased the expression of protease-activated receptor 4 mRNA and protein in dorsal root ganglion neurons.Neurochem Res. 2013 Sep;38(9):1895-903. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1095-z. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23775412
-
Peripheral mechanisms of chronic pain.Med Rev (2021). 2022 Jun 27;2(3):251-270. doi: 10.1515/mr-2022-0013. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Med Rev (2021). 2022. PMID: 36067122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between cannabinoids and the neuroimmune system in migraine.J Headache Pain. 2024 Oct 16;25(1):178. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01883-3. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39407099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdulla FA, Smith PA. Axotomy- and autotomy-induced changes in the excitability of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2001;85:630–643. - PubMed
-
- Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN. A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature. 1996;379:257–262. - PubMed
-
- Amaya F, Wang H, Costigan M, Allchorne AJ, Hatcher JP, Egerton J, Stean T, Morisset V, Grose D, Gunthorpe MJ, Chessell IP, Tate S, Green PJ, Woolf CJ. The voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v) 1.9 is an effector of peripheral inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci. 2006;26:12852–12860. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
