Functional genomics in zebrafish permits rapid characterization of novel platelet membrane proteins
- PMID: 19109564
- PMCID: PMC2680375
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-162693
Functional genomics in zebrafish permits rapid characterization of novel platelet membrane proteins
Abstract
In this study, we demonstrate the suitability of the vertebrate Danio rerio (zebrafish) for functional screening of novel platelet genes in vivo by reverse genetics. Comparative transcript analysis of platelets and their precursor cell, the megakaryocyte, together with nucleated blood cell elements, endothelial cells, and erythroblasts, identified novel platelet membrane proteins with hitherto unknown roles in thrombus formation. We determined the phenotype induced by antisense morpholino oligonucleotide (MO)-based knockdown of 5 of these genes in a laser-induced arterial thrombosis model. To validate the model, the genes for platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb and the coagulation protein factor VIII were targeted. MO-injected fish showed normal thrombus initiation but severely impaired thrombus growth, consistent with the mouse knockout phenotypes, and concomitant knockdown of both resulted in spontaneous bleeding. Knockdown of 4 of the 5 novel platelet proteins altered arterial thrombosis, as demonstrated by modified kinetics of thrombus initiation and/or development. We identified a putative role for BAMBI and LRRC32 in promotion and DCBLD2 and ESAM in inhibition of thrombus formation. We conclude that phenotypic analysis of MO-injected zebrafish is a fast and powerful method for initial screening of novel platelet proteins for function in thrombosis.
Figures

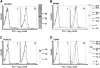

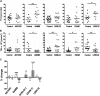
 ) using Cox regression and linear mixed modeling, respectively, as described in “Statistical analysis of the thrombosis model” (*P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .001). †TTA data for each DCBLD2 MO were significantly different and therefore were not combined. ††Results for TSA are applicable for esam sp1 only. Detailed P values for the combined and individual MO analysis are presented in Table 3.
) using Cox regression and linear mixed modeling, respectively, as described in “Statistical analysis of the thrombosis model” (*P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .001). †TTA data for each DCBLD2 MO were significantly different and therefore were not combined. ††Results for TSA are applicable for esam sp1 only. Detailed P values for the combined and individual MO analysis are presented in Table 3.Comment in
-
Comparative genomics: fishing nets hemostatic catch.Blood. 2009 May 7;113(19):4479-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-203117. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19423736 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gnatenko DV, Dunn JJ, McCorkle SR, Weissmann D, Perrotta PL, Bahou WF. Transcript profiling of human platelets using microarray and serial analysis of gene expression. Blood. 2003;101:2285–2293. - PubMed
-
- Watkins NA, Gusnanto A, de Bono B, et al. The HaemAtlas: characterizing gene expression in differentiated human blood cells. Blood. 2009;113:e1–e9. http://bloodjournal.hematologylibrary.org/cgi/content/full/113/19/e1; DOI . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

