Effect of peptides derived from food proteins on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 19109662
- PMCID: PMC2596738
- DOI: 10.3402/fnr.v52i0.1641
Effect of peptides derived from food proteins on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: In clinical trials, peptides derived from food proteins have shown an effect on blood pressure. This biological mechanism is mainly due to inhibition of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE), thereby regulating blood pressure through the renin-angiotensin system. A meta-analysis of these trials is needed to better quantify their effect, sources of variation, and possible publication bias.
Objective: To perform a meta-analysis of placebo-controlled clinical trials on peptides derived from food proteins and their effect on blood pressure.
Design: Trials identified using a defined search strategy in PubMed were included in the meta-analysis, and their pooled effect was estimated with a random effects model.
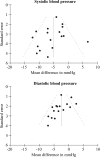
Results: Pooled effect of peptides was -5.13 mmHg (95% CI: -7.12, -3.14) for systolic blood pressure, and -2.42 mmHg (95% CI: -3.82, -1.03) for diastolic blood pressure. There were indications of publication bias for diastolic blood pressure data.
Conclusions: Peptides derived from food proteins may lead to significantly reduced blood pressure and could therefore be a supplement or alternative to pharmaceutical treatment for mild hypertension. Their effect seems more pronounced, or at least comparable, to that of other food components studied by randomized controlled trials. A high proportion of the reported trials was carried out using the well-known ACE inhibiting tripeptides - Valine-Proline-Proline (VPP) and Isoleucine-Proline-Proline (IPP).
Keywords: angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE); clinical trials; hypertension.
Figures



References
-
- Kearney P, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–23. - PubMed
-
- Krousel-Wood MA, Munther P, He J, Whelton PK. Primary prevention of essential hypertension. Med Clin North Am. 2004;88:223–38. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto N, Ejiri M, Mizuno S. Biogenic peptides and their potential use. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:1345–55. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Fandiño R, Otte J, van Camp J. Physiological, chemical and technological aspects of milk-protein-derived peptides with antihypertensive and ACE-inhibitory activity. Int Dairy J. 2006;16:1277–93.
-
- Glass GV. Primary, secondary and meta-analysis of research. Educ Res. 1976;5(10):3–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

