Disruption of colonic barrier function and induction of mediator release by strains of Campylobacter jejuni that invade epithelial cells
- PMID: 19109868
- PMCID: PMC2778118
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.7345
Disruption of colonic barrier function and induction of mediator release by strains of Campylobacter jejuni that invade epithelial cells
Abstract
Aim: To study the mechanisms by which Campylobacter jejuni (C. jejuni) causes inflammation and diarrhea. In particular, direct interactions with intestinal epithelial cells and effects on barrier function are poorly under-stood.
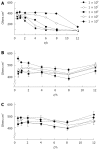
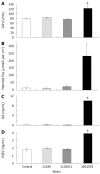
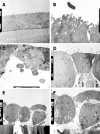
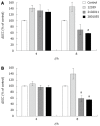
Methods: To model the initial pathogenic effects of C. jejuni on intestinal epithelium, polarized human colonic HCA-7 monolayers were grown on permeabilized filters and infected apically with clinical isolates of C. jejuni. Integrity of the monolayer was monitored by changes in monolayer resistance, release of lactate dehydrogenase, mannitol fluxes and electron microscopy. Invasion of HCA-7 cells was assessed by a modified gentamicin protection assay, translocation by counting colony forming units in the basal chamber, stimulation of mediator release by immunoassays and secretory responses in monolayers stimulated by bradykinin in an Ussing chamber.
Results: All strains translocated across monolayers but only a minority invaded HCA-7 cells. Strains that invaded HCA-7 cells destroyed monolayer resistance over 6 h, accompanied by increased release of lactate dehydrogenase, a four-fold increase in permeability to [(3)H] mannitol, and ultrastructural disruption of tight junctions, with rounding and lifting of cells off the filter membrane. Synthesis of interleukin (IL)-8 and prostaglandin E(2) was increased with strains that invaded the monolayer but not with those that did not.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate two distinct effects of C. jejuni on colonic epithelial cells and provide an informative model for further investigation of initial host cell responses to C. jejuni.
Figures

References
-
- Snelling WJ, Matsuda M, Moore JE, Dooley JS. Campylobacter jejuni. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2005;41:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Young KT, Davis LM, Dirita VJ. Campylobacter jejuni: molecular biology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:665–679. - PubMed
-
- Dorrell N, Wren BW. The second century of Campylobacter research: recent advances, new opportunities and old problems. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2007;20:514–518. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen F, Bailey R, Williams S, Henderson P, Wareing DR, Bolton FJ, Frost JA, Ward L, Humphrey TJ. Prevalence and numbers of Salmonella and Campylobacter spp. on raw, whole chickens in relation to sampling methods. Int J Food Microbiol. 2002;76:151–164. - PubMed
-
- Yao R, Burr DH, Guerry P. CheY-mediated modulation of Campylobacter jejuni virulence. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:1021–1031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

