Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway
- PMID: 19109899
- PMCID: PMC2621059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.044
Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway
Abstract
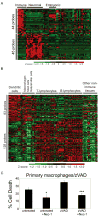
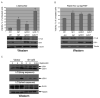
Stimulation of death receptors by agonists such as FasL and TNFalpha activates apoptotic cell death in apoptotic-competent conditions or a type of necrotic cell death dependent on RIP1 kinase, termed necroptosis, in apoptotic-deficient conditions. In a genome-wide siRNA screen for regulators of necroptosis, we identify a set of 432 genes that regulate necroptosis, a subset of 32 genes that act downstream and/or as regulators of RIP1 kinase, 32 genes required for death-receptor-mediated apoptosis, and 7 genes involved in both necroptosis and apoptosis. We show that the expression of subsets of the 432 genes is enriched in the immune and nervous systems, and cellular sensitivity to necroptosis is regulated by an extensive signaling network mediating innate immunity. Interestingly, Bmf, a BH3-only Bcl-2 family member, is required for death-receptor-induced necroptosis. Our study defines a cellular signaling network that regulates necroptosis and the molecular bifurcation that controls apoptosis and necroptosis.
Figures




Comment in
-
Necroptosis: a specialized pathway of programmed necrosis.Cell. 2008 Dec 26;135(7):1161-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.004. Cell. 2008. PMID: 19109884
References
-
- Cheng KW, Lahad JP, Kuo WL, Lapuk A, Yamada K, Auersperg N, Liu J, Smith-McCune K, Lu KH, Fishman D, et al. The RAB25 small GTPase determines aggressiveness of ovarian and breast cancers. Nat Med. 2004;10:1251–1256. - PubMed
-
- Clarke PG. Developmental cell death: morphological diversity and multiple mechanisms. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1990;181:195–213. - PubMed
-
- Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:112–119. - PubMed
-
- Fiers W, Beyaert R, Boone E, Cornelis S, Declercq W, Decoster E, Denecker G, Depuydt B, De Valck D, De Wilde G, et al. TNF-induced intracellular signaling leading to gene induction or to cytotoxicity by necrosis or by apoptosis. J Inflamm. 1995;47:67–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

