Secreted frizzled related protein 2 protects cells from apoptosis by blocking the effect of canonical Wnt3a
- PMID: 19109969
- PMCID: PMC2710029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.11.016
Secreted frizzled related protein 2 protects cells from apoptosis by blocking the effect of canonical Wnt3a
Abstract
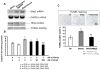
We have demonstrated that mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing the survival gene Akt can confer paracrine protection to ischemic myocytes both in vivo and in vitro through the release of secreted frizzled related protein 2 (Sfrp2). However, the mechanisms mediating these effects of Sfrp2 have not been fully elucidated. In this study, we studied rat cardiomyoblasts subjected to hypoxia reoxygenation (HR) injury to test the hypothesis that Sfrp2 exerts anti-apoptotic effect by antagonizing pro-apoptotic properties of specific Wnt ligands. We examined the effect of Wnt3a and Sfrp2 on HR-induced apoptosis. Wnt3a significantly increased cellular caspase activities and TUNEL staining in response to HR. Sfrp2 attenuated significantly Wnt3a-induced caspase activities in a concentration dependent fashion. Using a solid phase binding assay, our data demonstrates that Sfrp2 physically binds to Wnt3a. In addition, we observed that Sfrp2 dramatically inhibits the beta-catenin/TCF transcriptional activities induced by Wnt3a. Impressively, Dickkopf-1, a protein that binds to the Wnt coreceptor LRP, significantly inhibited the Wnt3a-activated caspase and transcriptional activities. Similarly, siRNA against beta-catenin markedly inhibited the Wnt3a-activated caspase activities. Consistent with this, significantly fewer TUNEL positive cells were observed in siRNA transfected cells than in control cells. Together, our data provide strong evidence to support the notion that Wnt3a is a canonical Wnt with pro-apoptotic action whose cellular activity is prevented by Sfrp2 through, at least in part, the direct binding of these molecules. These results can explain the in vivo protective effect of Sfrp2 and highlight its therapeutic potential for the ischemic heart.
Figures


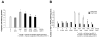

References
-
- Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, He H, Rezvani M, Ingwall JS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt Prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 2003 Sep;9(9):1195–1201. - PubMed
-
- Gnecchi M, He H, Liang OD, Melo LG, Morello F, Mu H, et al. Paracrine action acconts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Med. 2005 Apr;11(4):367–368. - PubMed
-
- Dann CE, Hsieh JC, Rattner A, Sharma D, Nathans J, Leahy DJ. Insights into Wnt binding and signaling from the structures of two Frizzled cysteine-rich domains. Nature. 2001 Jul 5;412(6842):86–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

