Structure of a complete integrin ectodomain in a physiologic resting state and activation and deactivation by applied forces
- PMID: 19111664
- PMCID: PMC2758073
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.11.018
Structure of a complete integrin ectodomain in a physiologic resting state and activation and deactivation by applied forces
Abstract
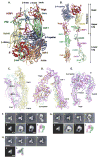
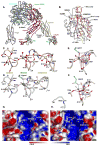
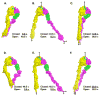
The complete ectodomain of integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) reveals a bent, closed, low-affinity conformation, the beta knee, and a mechanism for linking cytoskeleton attachment to high affinity for ligand. Ca and Mg ions in the recognition site, including the synergistic metal ion binding site (SyMBS), are loaded prior to ligand binding. Electrophilicity of the ligand-binding Mg ion is increased in the open conformation. The beta(3) knee passes between the beta(3)-PSI and alpha(IIb)-knob to bury the lower beta leg in a cleft, from which it is released for extension. Different integrin molecules in crystals and EM reveal breathing that appears on pathway to extension. Tensile force applied to the extended ligand-receptor complex stabilizes the closed, low-affinity conformation. By contrast, an additional lateral force applied to the beta subunit to mimic attachment to moving actin filaments stabilizes the open, high-affinity conformation. This mechanism propagates allostery over long distances and couples cytoskeleton attachment of integrins to their high-affinity state.
Figures
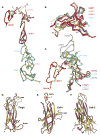
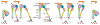
References
-
- Alon R, Dustin ML. Force as a Facilitator of Integrin Conformational Changes during Leukocyte Arrest on Blood Vessels and Antigen-Presenting Cells. Immunity. 2007;26:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Arnaout MA, Mahalingam B, Xiong JP. Integrin structure, allostery, and bidirectional signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:381–410. - PubMed
-
- Beglova N, Blacklow SC, Takagi J, Springer TA. Cysteine-rich module structure reveals a fulcrum for integrin rearrangement upon activation. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9:282–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

