Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model
- PMID: 19111880
- PMCID: PMC2650425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.12.006
Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model
Erratum in
- Cancer Cell. 2009 Mar 3;15(3):240
Abstract
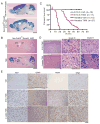
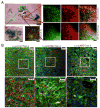
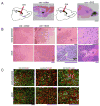
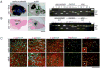
Malignant astrocytomas are infiltrative and incurable brain tumors. Despite profound therapeutic implications, the identity of the cell (or cells) of origin has not been rigorously determined. We previously reported mouse models based on conditional inactivation of the human astrocytoma-relevant tumor suppressors p53, Nf1, and Pten, wherein through somatic loss of heterozygosity, mutant mice develop tumors with 100% penetrance. In the present study, we show that tumor suppressor inactivation in neural stem/progenitor cells is both necessary and sufficient to induce astrocytoma formation. We demonstrate in vivo that transformed cells and their progeny undergo infiltration and multilineage differentiation during tumorigenesis. Tumor suppressor heterozygous neural stem/progenitor cultures from presymptomatic mice show aberrant growth advantage and altered differentiation, thus identifying a pretumorigenic cell population.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, Tang Y, DeFrances J, Stover E, Weissleder R, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:269–277. - PubMed
-
- Correa-Cerro LS, Mandell JW. Molecular mechanisms of astrogliosis: new approaches with mouse genetics. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007;66:169–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

