Efficient mitochondrial targeting relies on co-operation of multiple protein signals in plants
- PMID: 19112171
- PMCID: PMC2652046
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ern319
Efficient mitochondrial targeting relies on co-operation of multiple protein signals in plants
Abstract
To date, the most prevalent model for transport of pre-proteins to plant mitochondria is based on the activity of an N-terminal extension serving as a targeting peptide. Whether the efficient delivery of proteins to mitochondria is based exclusively on the action of the N-terminal extension or also on that of other protein determinants has yet to be defined. A novel mechanism is reported here for the targeting of a plant protein, named MITS1, to mitochondria. It was found that MITS1 contains an N-terminal extension that is responsible for mitochondrial targeting. Functional dissection of this extension shows the existence of a cryptic signal for protein targeting to the secretory pathway. The first 11 amino acids of the N-terminal extension are necessary to overcome the activity of this signal sequence and target the protein to the mitochondria. These data suggest that co-operation of multiple determinants within the N-terminal extension of mitochondrial proteins may be necessary for efficient mitochondrial targeting. It was also established that the presence of a tryptophan residue toward the C-terminus of the protein is crucial for mitochondrial targeting, as mutation of this residue results in a redistribution of MITS1 to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. These data suggest a novel targeting model whereby protein traffic to plant mitochondria is influenced by domains in the full-length protein as well as the N-terminal extension.
Figures
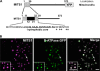

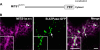


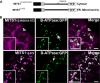
Comment in
-
Known knowns, known unknowns, unknown unknowns and the propagation of scientific enquiry.J Exp Bot. 2009;60(3):712-4. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp043. J Exp Bot. 2009. PMID: 19269994 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alder NN, Johnson AE. Cotranslational membrane protein biogenesis at the endoplasmic reticulum. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279:22787–22790. - PubMed
-
- Bannai H, Tamada Y, Maruyama O, Nakai K, Miyano S. Extensive feature detection of N-terminal protein sorting signals. Bioinformatics. 2002;18:298–305. - PubMed
-
- Boevink P, Oparka K, Santa Cruz S, Martin B, Betteridge A, Hawes C. Stacks on tracks: the plant Golgi apparatus traffics on an actin/ER network. The Plant Journal. 1998;15:441–447. - PubMed

