Distinct effects of tafazzin deletion in differentiated and undifferentiated mitochondria
- PMID: 19114128
- PMCID: PMC2660382
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mito.2008.12.001
Distinct effects of tafazzin deletion in differentiated and undifferentiated mitochondria
Abstract
Tafazzin is a conserved mitochondrial protein that is required to maintain normal content and composition of cardiolipin. We used electron tomography to investigate the effect of tafazzin deletion on mitochondrial structure and found that cellular differentiation plays a crucial role in the manifestation of abnormalities. This conclusion was reached by comparing differentiated cardiomyocytes with embryonic stem cells from mouse and by comparing different tissues from Drosophila melanogaster. The data suggest that tafazzin deficiency affects cardiolipin in all mitochondria, but significant alterations of the ultrastructure, such as remodeling and aggregation of inner membranes, will only occur after specific differentiation.
Figures


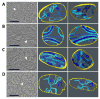
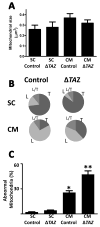
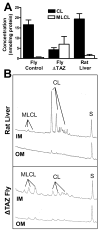

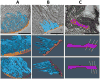
References
-
- Barth PG, Scholte HR, Berden JA, Van der Klei-Van Moorsel JM, Luyt-Houwen IE, Van’t Veer-Korthof ET, Van der Harten JJ, Sobotka-Plojhar MA. An X-linked mitochondrial disease affecting cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle and neutrophil leucocytes. J Neurol Sci. 1983;62:327–355. - PubMed
-
- Barth PG, Wanders RJ, Vreken P, Janssen EA, Lam J, Baas F. X-linked cardioskeletal myopathy and neutropenia (Barth syndrome) J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999;22:555–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

