T-POP array identifies EcnR and PefI-SrgD as novel regulators of flagellar gene expression
- PMID: 19114490
- PMCID: PMC2648201
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01177-08
T-POP array identifies EcnR and PefI-SrgD as novel regulators of flagellar gene expression
Abstract
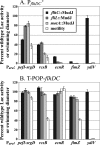
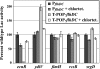
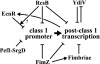
The T-POP transposon was employed in a general screen for tetracycline (Tet)-induced chromosomal loci that exhibited Tet-activated or Tet-repressed expression of a fliC-lac transcriptional fusion. Insertions that activated flagellar transcription were located in flagellar genes. T-POP insertions that exhibited Tet-dependent fliC-lac inhibition were isolated upstream of the ecnR, fimZ, pefI-srgD, rcsB, and ydiV genes and in the flagellar gene flgA, which is located upstream of the anti-sigma(28) factor gene flgM. When expressed from the chromosomal P(araBAD) promoter, EcnR, FimZ, PefI-SrgD, and RcsB inhibited the transcription of the flagellar class 1 flhDC operon. YdiV, which is weakly homologous to EAL domain proteins involved in cyclic-di-GMP regulation, appears to act at a step after class 1 transcription. By using a series of deletions of the regulatory genes to try to disrupt each pathway, these regulators were found to act largely independently of one another. These results identify EcnR and PefI-SrgD as additional components of the complex regulatory network controlling flagellar expression.
Figures




Similar articles
-
RflM functions as a transcriptional repressor in the autogenous control of the Salmonella Flagellar master operon flhDC.J Bacteriol. 2013 Sep;195(18):4274-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.00728-13. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23873910 Free PMC article.
-
Completion of the hook-basal body complex of the Salmonella typhimurium flagellum is coupled to FlgM secretion and fliC transcription.Mol Microbiol. 2000 Sep;37(5):1220-31. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02081.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10972838
-
EAL domain protein YdiV acts as an anti-FlhD4C2 factor responsible for nutritional control of the flagellar regulon in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2011 Apr;193(7):1600-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.01494-10. Epub 2011 Jan 28. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21278297 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering bacterial flagellar gene regulatory networks in the genomic era.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2009;67:257-95. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2164(08)01008-3. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19245942 Review.
-
Coupling of flagellar gene expression to flagellar assembly in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and Escherichia coli.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2000 Dec;64(4):694-708. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.64.4.694-708.2000. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2000. PMID: 11104815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Novel Factors Involved in Swimming and Swarming Motility in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 12;10(8):e0135351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135351. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26267246 Free PMC article.
-
The transcript from the σ(28)-dependent promoter is translationally inert in the expression of the σ(28)-encoding gene fliA in the fliAZ operon of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2011 Nov;193(22):6132-41. doi: 10.1128/JB.05909-11. Epub 2011 Sep 9. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21908664 Free PMC article.
-
RflM functions as a transcriptional repressor in the autogenous control of the Salmonella Flagellar master operon flhDC.J Bacteriol. 2013 Sep;195(18):4274-82. doi: 10.1128/JB.00728-13. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23873910 Free PMC article.
-
Mutually repressing repressor functions and multi-layered cellular heterogeneity regulate the bistable Salmonella fliC census.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Dec;94(6):1272-84. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12828. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25315056 Free PMC article.
-
Flagella-independent surface motility in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 10;112(6):1850-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422938112. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25624475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arricau, N., D. Hermant, H. Waxin, C. Ecobichon, P. S. Duffey, and M. Y. Popoff. 1998. The RcsB-RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol. Microbiol. 29835-850. - PubMed
-
- Beloin, C., and J. M. Ghigo. 2005. Finding gene-expression patterns in bacterial biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 1316-19. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, R. E., B. K. Leskiw, R. S. Hodges, C. M. Kay, and J. H. Weiner. 1998. The entericidin locus of Escherichia coli and its implications for programmed bacterial cell death. J. Mol. Biol. 280583-596. - PubMed
-
- Campoy, S., M. Jara, N. Busquets, A. M. de Rozas, I. Badiola, and J. Barbé. 2002. Intracellular cyclic AMP concentration is decreased in Salmonella typhimurium fur mutants. Microbiology 1481039-1048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

