Ras subcellular localization defines extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 substrate specificity through distinct utilization of scaffold proteins
- PMID: 19114553
- PMCID: PMC2643815
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01359-08
Ras subcellular localization defines extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 substrate specificity through distinct utilization of scaffold proteins
Abstract
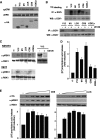
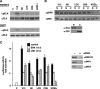
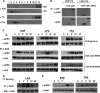
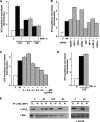
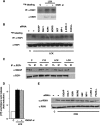
Subcellular localization influences the nature of Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signals by unknown mechanisms. Herein, we demonstrate that the microenvironment from which Ras signals emanate determines which substrates will be preferentially phosphorylated by the activated ERK1/2. We show that the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFr) and cytosolic phospholipase A(2) (cPLA(2)) is most prominent when ERK1/2 are activated from lipid rafts, whereas RSK1 is mainly activated by Ras signals from the disordered membrane. We present evidence indicating that the underlying mechanism of this substrate selectivity is governed by the participation of different scaffold proteins that distinctively couple ERK1/2, activated at defined microlocalizations, to specific substrates. As such, we show that for cPLA(2) activation, ERK1/2 activated at lipid rafts interact with KSR1, whereas ERK1/2 activated at the endoplasmic reticulum utilize Sef-1. To phosphorylate the EGFr, ERK1/2 activated at lipid rafts require the participation of IQGAP1. Furthermore, we demonstrate that scaffold usage markedly influences the biological outcome of Ras site-specific signals. These results disclose an unprecedented spatial regulation of ERK1/2 substrate specificity, dictated by the microlocalization from which Ras signals originate and by the selection of specific scaffold proteins.
Figures






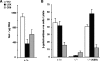
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking and RSK activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jul;23(14):4796-804. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4796-4804.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12832467 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystokinin stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase through activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, Yes, and protein kinase C. Signal amplification at the level of Raf by activation of protein kinase Cepsilon.J Biol Chem. 2003 Feb 28;278(9):7065-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211234200. Epub 2002 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12496267
-
Signal strength dictates phosphoinositide 3-kinase contribution to Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 activation via differential Gab1/Shp2 recruitment: consequences for resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;28(2):587-600. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01318-07. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18025104 Free PMC article.
-
How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer?Cell Cycle. 2009 Apr 15;8(8):1168-75. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.8.8147. Epub 2009 Apr 11. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19282669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK1/2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Aug;66(2):105-43. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 22569528 Review.
Cited by
-
RAS Subcellular Localization Inversely Regulates Thyroid Tumor Growth and Dissemination.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 10;12(9):2588. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092588. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32927904 Free PMC article.
-
Non-stimulated, agonist-stimulated and store-operated Ca2+ influx in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells and the effect of EGF-induced EMT on calcium entry.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036923. Epub 2012 May 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22666335 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic ERK2 Phosphorylates and Regulates Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 In Vitro and in Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Nov;54(9):7156-7170. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0225-4. Epub 2016 Oct 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27796752 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine withdrawal stress modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 12 p40 (IL-12p40) expression by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, which is further potentiated by glucocorticoids.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 26;286(34):29806-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.271460. Epub 2011 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21730055 Free PMC article.
-
Ras/MAPK signaling from endomembranes.Mol Oncol. 2009 Aug;3(4):297-307. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Jun 26. Mol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19615955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ait-Mamar, B., M. Cailleret, C. Rucker-Martin, A. Bouabdallah, G. Candiani, C. Adamy, P. Duvaldestin, F. Pecker, N. Defer, and C. Pavoine. 2005. The cytosolic phospholipase A2 pathway, a safeguard of beta2-adrenergic cardiac effects in rat. J. Biol. Chem. 28018881-18890. - PubMed
-
- Ajenjo, N., E. Canon, I. Sanchez-Perez, D. Matallanas, J. Leon, R. Perona, and P. Crespo. 2004. Subcellular localization determines the protective effects of activated ERK2 against distinct apoptogenic stimuli in myeloid leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 27932813-32823. - PubMed
-
- Arozarena, I., D. S. Aaronson, D. Matallanas, V. Sanz, N. Ajenjo, S. P. Tenbaum, H. Teramoto, T. Ighishi, J. C. Zabala, J. S. Gutkind, and P. Crespo. 2000. The Rho family GTPase Cdc42 regulates the activation of Ras/MAP kinase by the exchange factor Ras-GRF. J. Biol. Chem. 27526441-26448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
