Direct link between RACK1 function and localization at the ribosome in vivo
- PMID: 19114558
- PMCID: PMC2648249
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01718-08
Direct link between RACK1 function and localization at the ribosome in vivo
Abstract
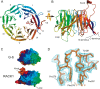
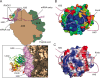
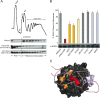
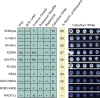
The receptor for activated C-kinase (RACK1), a conserved protein implicated in numerous signaling pathways, is a stoichiometric component of eukaryotic ribosomes located on the head of the 40S ribosomal subunit. To test the hypothesis that ribosome association is central to the function of RACK1 in vivo, we determined the 2.1-A crystal structure of RACK1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Asc1p) and used it to design eight mutant versions of RACK1 to assess roles in ribosome binding and in vivo function. Conserved charged amino acids on one side of the beta-propeller structure were found to confer most of the 40S subunit binding affinity, whereas an adjacent conserved and structured loop had little effect on RACK1-ribosome association. Yeast mutations that confer moderate to strong defects in ribosome binding mimic some phenotypes of a RACK1 deletion strain, including increased sensitivity to drugs affecting cell wall biosynthesis and translation elongation. Furthermore, disruption of RACK1's position at the 40S ribosomal subunit results in the failure of the mRNA binding protein Scp160 to associate with actively translating ribosomes. These results provide the first direct evidence that RACK1 functions from the ribosome, implying a physical link between the eukaryotic ribosome and cell signaling pathways in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Abramoff, M. D., P. J. Magelhaes, and S. J. Ram. 2004. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 1136-42.
-
- Adams, P. D., R. W. Grosse-Kunstleve, L. W. Hung, T. R. Ioerger, A. J. McCoy, N. W. Moriarty, R. J. Read, J. C. Sacchettini, N. K. Sauter, and T. C. Terwilliger. 2002. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 581948-1954. - PubMed
-
- Armon, A., D. Graur, and N. Ben-Tal. 2001. ConSurf: an algorithmic tool for the identification of functional regions in proteins by surface mapping of phylogenetic information. J. Mol. Biol. 307447-463. - PubMed
-
- Basmaji, F., H. Martin-Yken, F. Durand, A. Dagkessamanskaia, C. Pichereaux, M. Rossignol, and J. Francois. 2006. The ‘interactome’ of the Knr4/Smi1, a protein implicated in coordinating cell wall synthesis with bud emergence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Genet. Genomics 275217-230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
