Changing mortality risk associated with CD4 cell response to antiretroviral therapy in South Africa
- PMID: 19114870
- PMCID: PMC3776050
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328321823f
Changing mortality risk associated with CD4 cell response to antiretroviral therapy in South Africa
Abstract
Objective: To determine the relationship between mortality risk and the CD4 cell response to antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Design: Observational community-based ART cohort in South Africa.
Methods: CD4 cell counts were measured 4 monthly, and deaths were prospectively ascertained. Cumulative person-time accrued within a range of updated CD4 cell count strata (CD4 cell-strata) was calculated and used to derive CD4 cell-stratified mortality rates.
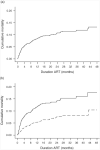
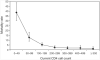
Results: Patients (2423) (median baseline CD4 cell count of 105 cells/microl) were observed for up to 5 years of ART. One hundred and ninety-seven patients died during 3155 person-years of observation. In microltivariate analysis, mortality rate ratios associated with 0-49, 50-99, 100-199, 200-299, 300-399, 400-499 and at least 500 cells/microl updated CD4 cell-strata were 11.6, 4.9, 2.6, 1.7, 1.5, 1.4 and 1.0, respectively. Analysis of CD4 cell count recovery permitted calculations of person-time accrued within these CD4 cell-strata. Despite rapid immune recovery, high mortality in the first year of ART was related to the large proportion of person-time accrued within CD4 cell-strata less than 200 cells/microl. Moreover, patients with baseline CD4 cell counts less than 100 cells/microl had much higher cumulative mortality estimates at 1 and 4 years (11.6 and 16.7%) compared with those of patients with baseline counts of at least 100 cells/microl (5.2 and 9.5%) largely because of greater cumulative person-time at CD4 cell counts less than 200 cells/microl.
Conclusion: Updated CD4 cell counts are the variable most strongly associated with mortality risk during ART. High cumicrolative mortality risk is associated with person-time accrued at low CD4 cell counts. National HIV programmes in resource-limited settings should be designed to minimize the time patients spend with CD4 cell counts less than 200 cells/microl both before and during ART.
Conflict of interest statement
There were no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS/WHO. AIDS epidemic update. 2007 http://data.unaids.org/pub/EPISlides/2007/2007_epiupdate_en.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization. Towards universal access: scaling up priority HIV/AIDS interventions in the health sector:progress report. 2007 http://www.who.int/hiv/mediacentre/universal_access_progress_report_en.pdf.
-
- Braitstein P, Brinkhof MW, Dabis F, Schechter M, Boulle A, Miotti P, et al. Mortality of HIV-1-infected patients in the first year of antiretroviral therapy: comparison between low-income and high-income countries. Lancet. 2006;367:817–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

