Contribution of the striatum to the effects of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation in L-DOPA-treated hemiparkinsonian rats
- PMID: 19115412
- PMCID: PMC2670562
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.21978
Contribution of the striatum to the effects of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation in L-DOPA-treated hemiparkinsonian rats
Abstract
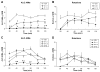
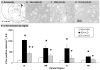
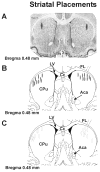
Clinical and experimental studies implicate the use of serotonin (5-HT)1A receptor agonists for the reduction of L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA)-induced dyskinesia (LID). Although raphe nuclei likely play a role in these antidyskinetic effects, an unexplored population of striatal 5-HT1A receptors (5-HT1AR) may also contribute. To better characterize this mechanism, L-DOPA-primed hemiparkinsonian rats received the 5-HT1AR agonist +/-8-OH-DPAT (0, 0.1, 1.0 mg/kg, i.p.) with or without cotreatment with the 5-HT1AR antagonist WAY100635 (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) 5 min after L-DOPA, after which abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs), rotations, and forelimb akinesia were quantified. To establish the effects of 5-HT1AR stimulation on L-DOPA-induced c-fos and preprodynorphin (PPD) mRNA within the dopamine-depleted striatum, immunohistochemistry and real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, respectively, were used. Finally, to determine the contribution of striatal 5-HT1AR to these effects, L-DOPA-primed hemiparkinsonian rats received bilateral intrastriatal microinfusions of +/-8-OH-DPAT (0, 5, or 10 microg/side), WAY100635 (5 microg/side), or both (10 microg + 5 microg/side) 5 min after L-DOPA, after which AIMs and rotations were examined. Systemic +/-8-OH-DPAT dose- and receptor-dependently attenuated L-DOPA-mediated AIMs and improved forelimb akinesia. Striatal c-fos immunoreactivity and PPD mRNA ipsilateral to the lesion were strongly induced by L-DOPA, while +/-8-OH-DPAT suppressed these effects. Finally, intrastriatal infusions of +/-8-OH-DPAT reduced AIMs while coinfusion of WAY100635 reversed its antidyskinetic effect. Collectively, these results support the hypothesis that the cellular and behavioral properties of 5-HT1AR agonists are conveyed in part via a population of functional 5-HT1AR within the striatum.
Copyright 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

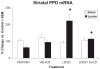
Similar articles
-
Effects of 5-HT1A receptor stimulation on D1 receptor agonist-induced striatonigral activity and dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian rats.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 May 15;4(5):747-60. doi: 10.1021/cn300234z. Epub 2013 Apr 1. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23496922 Free PMC article.
-
Striatal 5-HT1A receptor stimulation reduces D1 receptor-induced dyskinesia and improves movement in the hemiparkinsonian rat.Neuropharmacology. 2008 Dec;55(8):1321-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.031. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Neuropharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18824001 Free PMC article.
-
Local modulation of striatal glutamate efflux by serotonin 1A receptor stimulation in dyskinetic, hemiparkinsonian rats.Exp Neurol. 2011 Jun;229(2):288-99. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.02.012. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Exp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21352823 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of coincident 5-HT1A receptor stimulation and NMDA receptor antagonism on L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia and rotational behaviors in the hemi-parkinsonian rat.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Jul;199(1):99-108. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1135-6. Epub 2008 Jun 11. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18545986
-
Diverse serotonin actions of vilazodone reduce l-3,4-dihidroxyphenylalanine-induced dyskinesia in hemi-parkinsonian rats.Mov Disord. 2018 Nov;33(11):1740-1749. doi: 10.1002/mds.100. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 30485908
Cited by
-
Serotonin transporter inhibition attenuates l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia without compromising l-DOPA efficacy in hemi-parkinsonian rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Sep;36(6):2839-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08202.x. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22762478 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of BMY-14802 against L-DOPA- and dopamine agonist-induced dyskinesia in the hemiparkinsonian rat.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Jun;227(3):533-44. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3001-4. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 23389756 Free PMC article.
-
Striatal Nurr1, but not FosB expression links a levodopa-induced dyskinesia phenotype to genotype in Fisher 344 vs. Lewis hemiparkinsonian rats.Exp Neurol. 2020 Aug;330:113327. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113327. Epub 2020 May 5. Exp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32387398 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: A Novel Approach by Modulating 5-HT(1A) Receptors.Aging Dis. 2013 Feb;4(1):1-13. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Aging Dis. 2013. PMID: 23423244 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist Propranolol on dyskinesia and L-DOPA-induced striatal DA efflux in the hemi-parkinsonian rat.J Neurochem. 2015 Jul;134(2):222-32. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13125. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25866285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlskog JE, Muenter MD. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov Disord. 2001;16:448–458. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Westin JE, Cenci MA. Time course of striatal DeltaFosB-like immunoreactivity and prodynorphin mRNA levels after discontinuation of chronic dopaminomimetic treatment. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:661–666. - PubMed
-
- Antonelli T, Fuxe K, Tomasini MC, Bartoszyk GD, Seyfried CA, Tanganelli S, Ferraro L. Effects of sarizotan on the corticostriatal glutamate pathways. Synapse. 2005;58:193–199. - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Guigoni C, Hakansson K, Li Q, Dovero S, Barthe N, Bioulac BH, Gross CE, Fisone G, Bloch B, Bezard E. Increased D1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:17–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

