Isolation of Bordetella avium and novel Bordetella strain from patients with respiratory disease
- PMID: 19116056
- PMCID: PMC2660683
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1501.071677
Isolation of Bordetella avium and novel Bordetella strain from patients with respiratory disease
Abstract
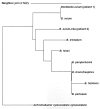
Bordetella avium is thought to be strictly an avian pathogen. However, 16S rRNA gene sequencing identified 2 isolates from 2 humans with respiratory disease as B. avium and a novel B. avium-like strain. Thus, B. avium and B. avium-like organisms are rare opportunistic human pathogens.
Figures
References
-
- Raffel TR, Register KB, Marks SA, Temple L. Prevalence of Bordetella avium infection in selected wild and domesticated birds in the eastern USA. J Wildl Dis. 2002;38:40–6. - PubMed
-
- Skeeles JK, Arp LH. Bordetellosis (turkey coryza). In: Calnek BW, Barnes HJ, Beard CW, McDougald LR, Saif YM, editors. Diseases of poultry. Ames (IA): Iowa State University Press; 1997. p. 275–87.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
