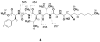Arenamides A-C, cytotoxic NFkappaB inhibitors from the marine actinomycete Salinispora arenicola
- PMID: 19117399
- PMCID: PMC2837138
- DOI: 10.1021/np800617a
Arenamides A-C, cytotoxic NFkappaB inhibitors from the marine actinomycete Salinispora arenicola
Erratum in
- J Nat Prod. 2010 Apr 23;73(4):796
Abstract
Three new cyclohexadepsipeptides, arenamides A-C (1-3), were isolated from the fermentation broth of a marine bacterial strain identified as Salinispora arenicola. The planar structures of these compounds were assigned by detailed interpretation of NMR and MS/MS spectroscopic data. The absolute configurations of the amino acids, and those of the chiral centers on the side chain, were established by application of the Marfey and modified Mosher methods. The effect of arenamides A and B on NFkappaB activity was studied with stably transfected 293/NFkappaB-Luc human embryonic kidney cells induced by treatment with tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Arenamides A (1) and B (2) blocked TNF-induced activation in a dose- and time-dependent manner with IC(50) values of 3.7 and 1.7 microM, respectively. In addition, the compounds inhibited nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) production with lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Moderate cytotoxicity was observed with the human colon carcinoma cell line HCT-116, but no cytotoxic effect was noted with cultured RAW cells. Taken together, these data suggest that the chemoprevention and anti-inflammatory characteristics of arenamides A and B warrant further investigation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases