The glycogen-binding domain on the AMPK beta subunit allows the kinase to act as a glycogen sensor
- PMID: 19117544
- PMCID: PMC2642990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.11.008
The glycogen-binding domain on the AMPK beta subunit allows the kinase to act as a glycogen sensor
Abstract
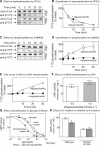
AMPK beta subunits contain a conserved domain that causes association with glycogen. Although glycogen availability is known to affect AMPK regulation in vivo, the molecular mechanism for this has not been clear. We now show that AMPK is inhibited by glycogen, particularly preparations with high branching content. We synthesized a series of branched oligosaccharides and show that those with a single alpha1-->6 branch are allosteric inhibitors that also inhibit phosphorylation by upstream kinases. Removal of the outer chains of glycogen using phosphorylase, thus exposing the outer branches, renders inhibition of AMPK more potent. Inhibition by all carbohydrates tested was dependent on the glycogen-binding domain being abolished by mutation of residues required for carbohydrate binding. Our results suggest the hypothesis that AMPK, as well as monitoring immediate energy availability by sensing AMP/ATP, may also be able to sense the status of cellular energy reserves in the form of glycogen.
Figures






Comment in
-
Branching out on AMPK Regulation.Cell Metab. 2009 Jan 7;9(1):7-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.12.007. Cell Metab. 2009. PMID: 19117541
References
-
- Aschenbach W.G., Suzuki Y., Breeden K., Prats C., Hirshman M.F., Dufresne S.D., Sakamoto K., Vilardo P.G., Steele M., Kim J.H. The muscle-specific protein phosphatase PP1G/R(GL)(G(M)) is essential for activation of glycogen synthase by exercise. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:39959–39967. - PubMed
-
- Carling D., Hardie D.G. The substrate and sequence specificity of the AMP-activated protein kinase. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1989;1012:81–86. - PubMed
-
- Danforth W.H. Glycogen synthetase activity in skeletal muscle. Interconversion of two forms and control of glycogen synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1965;240:588–593. - PubMed
-
- Davies S.P., Helps N.R., Cohen P.T.W., Hardie D.G. 5′-AMP inhibits dephosphorylation, as well as promoting phosphorylation, of the AMP-activated protein kinase. Studies using bacterially expressed human protein phosphatase-2Cα and native bovine protein phosphatase-2AC. FEBS Lett. 1995;377:421–425. - PubMed
-
- Derave W., Ai H., Ihlemann J., Witters L.A., Kristiansen S., Richter E.A., Ploug T. Dissociation of AMP-activated protein kinase activation and glucose transport in contracting slow-twitch muscle. Diabetes. 2000;49:1281–1287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

