Advances in the treatment of fragile X syndrome
- PMID: 19117905
- PMCID: PMC2888470
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2008-0317
Advances in the treatment of fragile X syndrome
Abstract
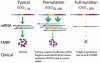
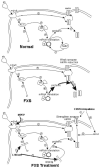
The FMR1 mutations can cause a variety of disabilities, including cognitive deficits, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, autism, and other socioemotional problems, in individuals with the full mutation form (fragile X syndrome) and distinct difficulties, including primary ovarian insufficiency, neuropathy and the fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome, in some older premutation carriers. Therefore, multigenerational family involvement is commonly encountered when a proband is identified with a FMR1 mutation. Studies of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 pathway antagonists in animal models of fragile X syndrome have demonstrated benefits in reducing seizures, improving behavior, and enhancing cognition. Trials of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 antagonists are beginning with individuals with fragile X syndrome. Targeted treatments, medical and behavioral interventions, genetic counseling, and family supports are reviewed here.
Figures

References
-
- Loesch DZ, Huggins RM, Hagerman RJ. Phenotypic variation and FMRP levels in fragile X. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004;10(1):31–41. - PubMed
-
- Tassone F, Hagerman RJ, Iklé DN, et al. FMRP expression as a potential prognostic indicator in fragile X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1999;84(3):250–261. - PubMed
-
- Pieretti M, Zhang FP, Fu YH, et al. Absence of expression of the FMR-1 gene in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991;66(4):817–822. - PubMed
-
- De Boulle K, Verkerk AJ, Reyniers E, et al. A point mutation in the FMR-1 gene associated with fragile X mental retardation. Nat Genet. 1993;3(1):31–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K12 RR017643/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR024146/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024146/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1KL2RR025009/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD036071/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD036071/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH077554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000455/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AG032115/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD002274/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 DE019583/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD058043/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH77554/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5K12RR017643/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HD02274/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD024061/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U50 DD000596/DD/NCBDD CDC HHS/United States
- HD24061/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 AG032115/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DE019583/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

