Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway predict for antitumor activity of the inhibitor PX-866 whereas oncogenic Ras is a dominant predictor for resistance
- PMID: 19117997
- PMCID: PMC2613546
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6656
Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway predict for antitumor activity of the inhibitor PX-866 whereas oncogenic Ras is a dominant predictor for resistance
Abstract
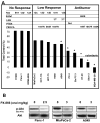
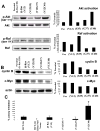
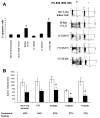
The novel phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor PX-866 was tested against 13 experimental human tumor xenografts derived from cell lines of various tissue origins. Mutant PI3K (PIK3CA) and loss of PTEN activity were sufficient, but not necessary, as predictors of sensitivity to the antitumor activity of the PI3K inhibitor PX-866 in the presence of wild-type Ras, whereas mutant oncogenic Ras was a dominant determinant of resistance, even in tumors with coexisting mutations in PIK3CA. The level of activation of PI3K signaling measured by tumor phosphorylated Ser(473)-Akt was insufficient to predict in vivo antitumor response to PX-866. Reverse-phase protein array revealed that the Ras-dependent downstream targets c-Myc and cyclin B were elevated in cell lines resistant to PX-866 in vivo. Studies using an H-Ras construct to constitutively and preferentially activate the three best-defined downstream targets of Ras, i.e., Raf, RalGDS, and PI3K, showed that mutant Ras mediates resistance through its ability to use multiple pathways for tumorigenesis. The identification of Ras and downstream signaling pathways driving resistance to PI3K inhibition might serve as an important guide for patient selection as inhibitors enter clinical trials and for the development of rational combinations with other molecularly targeted agents.
Figures


References
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science (New York, NY. 2002;296:1655–7. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Cohen P. Mechanism of activation and function of protein kinase B. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:55–62. - PubMed
-
- Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science (New York, NY. 2005;307:1098–101. - PubMed
-
- Meier R, Alessi DR, Cron P, Andjelkovic M, Hemmings BA. Mitogenic activation, phosphorylation, and nuclear translocation of protein kinase Bbeta. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1997;272:30491–7. - PubMed
-
- Nicholson KM, Anderson NG. The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cellular signalling. 2002;14:381–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA052995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 17094/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 95060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 99031/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA095060/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA090821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA099031/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 090821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK052825/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA098258/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA052995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA017094/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 52995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

